The role of CD44 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer development
- PMID: 26719706
- PMCID: PMC4689260
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S95470
The role of CD44 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer development
Abstract
CD44, a multi-structural and multifunctional transmembrane glycoprotein, was initially identified as a receptor for hyaluronan that participates in both physiological and pathological processes. CD44 is found to be closely linked to the development of various solid tumors. Molecular studies have revealed that high CD44 expression was correlated with the phenotypes of cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, thereby contributing to tumor invasion, metastasis, recurrence, and chemoresistance. Correspondingly, blockade of CD44 has been demonstrated to be capable of attenuating the malignant phenotype, slowing cancer progression, and reversing therapy resistance. Clinical analyses showed that high CD44 expression is associated with poor survival of various cancer patients, indicating that CD44 can be a potential prognostic marker. In this review, we summarize recent research progress of CD44 on tumor biology and the clinical significance of CD44.
Keywords: CD44; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; prognosis; tumor progression.
Figures
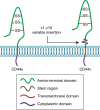
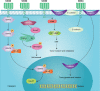
Similar articles
-
CD44 as a tumor biomarker and therapeutic target.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020 Dec 10;9(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40164-020-00192-0. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33303029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer stem-like cells enriched with CD29 and CD44 markers exhibit molecular characteristics with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma.Arch Dermatol Res. 2013 Jan;305(1):35-47. doi: 10.1007/s00403-012-1260-2. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013. PMID: 22740085
-
Combination of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like phenotypes has independent prognostic value in gastric cancer.Hum Pathol. 2012 Apr;43(4):520-8. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Hum Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22018628
-
Cancer stem cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers predict worse outcome in metaplastic carcinoma of the breast.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Feb;150(1):31-41. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3299-1. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25677743
-
The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: therapeutic implications.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 May 10;11(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0605-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29747682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SWAP-70 promotes glioblastoma cellular migration and invasion by regulating the expression of CD44s.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Nov 21;19:305. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-1035-3. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31832018 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition Markers and CD44 Isoforms Are Differently Expressed in 2D and 3D Cell Cultures of Prostate Cancer Cells.Cells. 2019 Feb 11;8(2):143. doi: 10.3390/cells8020143. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30754655 Free PMC article.
-
Commensal-infected macrophages induce dedifferentiation and reprogramming of epithelial cells during colorectal carcinogenesis.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 1;8(60):102176-102190. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22250. eCollection 2017 Nov 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29254234 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-200c Nanoparticles Sensitized Gastric Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy by Regulating PD-L1 Expression and EMT.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Nov 27;12:12215-12223. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S279978. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33273858 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor basis of biological activity of polysaccharides.Biophys Rev. 2023 Jul 27;15(5):1209-1222. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01102-4. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 37975017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rodrigo JP, Dominguez F, Alvarez C, Gonzalez MV, Herrero A, Suarez C. Clinicopathologic significance of expression of CD44s and CD44v6 isoforms in squamous cell carcinoma of the supraglottic larynx. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;118(1):67–72. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

