Activin Receptor-Like Kinase Receptors ALK5 and ALK1 Are Both Required for TGFβ-Induced Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 26720610
- PMCID: PMC4697836
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146124
Activin Receptor-Like Kinase Receptors ALK5 and ALK1 Are Both Required for TGFβ-Induced Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
Introduction: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) are promising for cartilage regeneration because BMSCs can differentiate into cartilage tissue-producing chondrocytes. Transforming Growth Factor β (TGFβ) is crucial for inducing chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs and is known to signal via Activin receptor-Like Kinase (ALK) receptors ALK5 and ALK1. Since the specific role of these two TGFβ receptors in chondrogenesis is unknown, we investigated whether ALK5 and ALK1 are expressed in BMSCs and whether both receptors are required for chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs.
Materials & methods: ALK5 and ALK1 gene expression in human BMSCs was determined with RT-qPCR. To induce chondrogenesis, human BMSCs were pellet-cultured in serum-free chondrogenic medium containing TGFβ1. Chondrogenesis was evaluated by aggrecan and collagen type IIα1 RT-qPCR analysis, and histological stainings of proteoglycans and collagen type II. To overexpress constitutively active (ca) receptors, BMSCs were transduced either with caALK5 or caALK1. Expression of ALK5 and ALK1 was downregulated by transducing BMSCs with shRNA against ALK5 or ALK1.
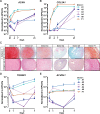
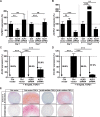
Results: ALK5 and ALK1 were expressed in in vitro-expanded as well as in pellet-cultured BMSCs from five donors, but mRNA levels of both TGFβ receptors did not clearly associate with chondrogenic induction. TGFβ increased ALK5 and decreased ALK1 gene expression in chondrogenically differentiating BMSC pellets. Neither caALK5 nor caALK1 overexpression induced cartilage matrix formation as efficient as that induced by TGFβ. Moreover, short hairpin-mediated downregulation of either ALK5 or ALK1 resulted in a strong inhibition of TGFβ-induced chondrogenesis.
Conclusion: ALK5 as well as ALK1 are required for TGFβ-induced chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs, and TGFβ not only directly induces chondrogenesis, but also modulates ALK5 and ALK1 receptor signaling in BMSCs. These results imply that optimizing cartilage formation by mesenchymal stem cells will depend on activation of both receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
ALK1 opposes ALK5/Smad3 signaling and expression of extracellular matrix components in human chondrocytes.J Bone Miner Res. 2008 Jun;23(6):896-906. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.080209. J Bone Miner Res. 2008. PMID: 18333754
-
Increase in ALK1/ALK5 ratio as a cause for elevated MMP-13 expression in osteoarthritis in humans and mice.J Immunol. 2009 Jun 15;182(12):7937-45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803991. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19494318
-
Reduced chondrogenic potential of adipose tissue derived stromal cells correlates with an altered TGFbeta receptor and BMP profile and is overcome by BMP-6.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jun;211(3):682-91. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20977. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17238135
-
Age-dependent alteration of TGF-β signalling in osteoarthritis.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jan;347(1):257-65. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1194-6. Epub 2011 Jun 4. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 21638205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A role for age-related changes in TGFbeta signaling in aberrant chondrocyte differentiation and osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(1):201. doi: 10.1186/ar2896. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20156325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activin and Nodal Are Not Suitable Alternatives to TGFβ for Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Cartilage. 2017 Oct;8(4):432-438. doi: 10.1177/1947603516667585. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Cartilage. 2017. PMID: 28934877 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Dose-Rate Radiation-Induced Secretion of TGF-β3 Together with an Activator in Small Extracellular Vesicles Modifies Low-Dose Hyper-Radiosensitivity through ALK1 Binding.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 24;23(15):8147. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158147. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897723 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid shear stress generates a unique signaling response by activating multiple TGFβ family type I receptors in osteocytes.FASEB J. 2021 Mar;35(3):e21263. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001998R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33570811 Free PMC article.
-
Activin receptor-like kinases: a diverse family playing an important role in cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 1;6(11):2431-2447. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27904762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The changing role of TGFβ in healthy, ageing and osteoarthritic joints.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017 Mar;13(3):155-163. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.219. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28148919 Review.
References
-
- Shelbourne KD, Jari S, Gray T. Outcome of untreated traumatic articular cartilage defects of the knee: a natural history study. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume. 2003;85-A Suppl 2:8–16. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

