Pathological α-synuclein distribution in subjects with coincident Alzheimer's and Lewy body pathology
- PMID: 26721587
- PMCID: PMC4754135
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-015-1526-9
Pathological α-synuclein distribution in subjects with coincident Alzheimer's and Lewy body pathology
Abstract
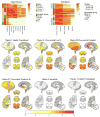
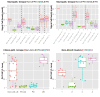
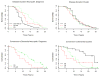
We investigated the distribution patterns of Lewy body-related pathology (LRP) and the effect of coincident Alzheimer disease (AD) pathology using a data-driven clustering approach that identified groups with different LRP pathology distributions without any diagnostic or researcher's input in two cohorts including: Parkinson disease patients without (PD, n = 141) and with AD (PD-AD, n = 80), dementia with Lewy bodies subjects without AD (DLB, n = 13) and demented subjects with AD and LRP pathology (Dem-AD-LB, n = 308). The Dem-AD-LB group presented two LRP patterns, olfactory-amygdala and limbic LRP with negligible brainstem pathology, that were absent in the PD groups, which are not currently included in the DLB staging system and lacked extracranial LRP as opposed to the PD group. The Dem-AD-LB individuals showed relative preservation of substantia nigra cells and dopamine active transporter in putamen. PD cases with AD pathology showed increased LRP. The cluster with occipital LRP was associated with non-AD type dementia clinical diagnosis in the Dem-AD-LB group and a faster progression to dementia in the PD groups. We found that (1) LRP pathology in Dem-AD-LB shows a distribution that differs from PD, without significant brainstem or extracranial LRP in initial phases; (2) coincident AD pathology is associated with increased LRP in PD indicating an interaction; (3) LRP and coincident AD pathology independently predict progression to dementia in PD, and (4) evaluation of LRP needs to acknowledge different LRP spreading patterns and evaluate substantia nigra integrity in the neuropathological assessment and consider the implications of neuropathological heterogeneity for clinical and biomarker characterization.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Classification; Dementia with Lewy bodies; Diagnosis; Neuropathology; Parkinson disease.
Figures


References
-
- Beach TG, Adler CH, Lue L, Sue LI, Bachalakuri J, Henry-Watson J, et al. Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;117(6):613–634. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0538-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS062684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS053488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS088341/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS062684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG05136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG19610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS088341/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

