Postnatal genome editing partially restores dystrophin expression in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 26721683
- PMCID: PMC4760628
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aad5725
Postnatal genome editing partially restores dystrophin expression in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy
Abstract
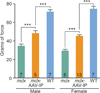
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing holds clinical potential for treating genetic diseases, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), which is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene. To correct DMD by skipping mutant dystrophin exons in postnatal muscle tissue in vivo, we used adeno-associated virus-9 (AAV9) to deliver gene-editing components to postnatal mdx mice, a model of DMD. Different modes of AAV9 delivery were systematically tested, including intraperitoneal at postnatal day 1 (P1), intramuscular at P12, and retro-orbital at P18. Each of these methods restored dystrophin protein expression in cardiac and skeletal muscle to varying degrees, and expression increased from 3 to 12 weeks after injection. Postnatal gene editing also enhanced skeletal muscle function, as measured by grip strength tests 4 weeks after injection. This method provides a potential means of correcting mutations responsible for DMD and other monogenic disorders after birth.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


Comment in
-
Genetic engineering: In vivo genome editing - growing in strength.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Mar;17(3):124. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.2. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 26781811 No abstract available.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 Flexes Its Muscles: In Vivo Somatic Gene Editing for Muscular Dystrophy.Mol Ther. 2016 Mar;24(3):414-6. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.29. Mol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26952918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL077439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099653/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-099653/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100401/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD 087351/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-077439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL-100401/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-111665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-093039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY012196/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD087351/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

