Infection of Immature Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) by Membrane Feeding
- PMID: 26721866
- PMCID: PMC5853672
- DOI: 10.1093/jme/tjv241
Infection of Immature Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) by Membrane Feeding
Abstract
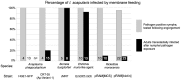
A reduction in the use of animals in infectious disease research is desirable for animal welfare as well as for simplification and standardization of experiments. An artificial silicone-based membrane-feeding system was adapted for complete engorgement of adult and nymphal Ixodes scapularis Say (Acari: Ixodidae), and for infecting nymphs with pathogenic, tick-borne bacteria. Six wild-type and genetically transformed strains of four species of bacteria were inoculated into sterile bovine blood and fed to ticks. Pathogens were consistently detected in replete nymphs by polymerase chain reaction. Adult ticks that ingested bacteria as nymphs were evaluated for transstadial transmission. Borrelia burgdorferi and Ehrlichia muris-like agent showed high rates of transstadial transmission to adult ticks, whereas Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Rickettsia monacensis demonstrated low rates of transstadial transmission/maintenance. Artificial membrane feeding can be used to routinely maintain nymphal and adult I. scapularis, and infect nymphs with tick-borne pathogens.
Figures



References
-
- Bonnet S., Jouglin M., Malandrin L., Becker C., Agoulon A., L’hostis M., Chauvin A. . 2007. . Transstadial and transovarial persistence of Babesia divergens DNA in Ixodes ricinus ticks fed on infected blood in a new skin-feeding technique . Parasitology 134 : 197 – 207 . - PubMed
-
- Bonnet S., Liu X. Y. . 2012. . Laboratory artificial infection of hard ticks: A tool for the analysis of tick-borne pathogen transmission . Acarologia 52 : 453 – 464 .
-
- Broadwater A. H., Sonenshine D. E., Hynes W. L., Ceraul S., De S.A.M. . 2002. . Glass capillary tube feeding: A method for infecting nymphal Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) with the lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi . J. Med. Entomol. 39 : 285 – 292 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

