Mucosal Administration of Collagen V Ameliorates the Atherosclerotic Plaque Burden by Inducing Interleukin 35-dependent Tolerance
- PMID: 26721885
- PMCID: PMC4751380
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.681882
Mucosal Administration of Collagen V Ameliorates the Atherosclerotic Plaque Burden by Inducing Interleukin 35-dependent Tolerance
Abstract
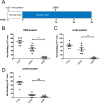
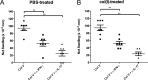
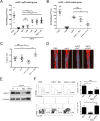
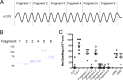
We have shown previously that collagen V (col(V)) autoimmunity is a consistent feature of atherosclerosis in human coronary artery disease and in the Apoe(-/-) mouse model. We have also shown sensitization of Apoe(-/-) mice with col(V) to markedly increase the atherosclerotic burden, providing evidence of a causative role for col(V) autoimmunity in atherosclerotic pathogenesis. Here we sought to determine whether induction of immune tolerance to col(V) might ameliorate atherosclerosis, providing further evidence for a causal role for col(V) autoimmunity in atherogenesis and providing insights into the potential for immunomodulatory therapeutic interventions. Mucosal inoculation successfully induced immune tolerance to col(V) with an accompanying reduction in plaque burden in Ldlr(-/-) mice on a high-cholesterol diet. The results therefore demonstrate that inoculation with col(V) can successfully ameliorate the atherosclerotic burden, suggesting novel approaches for therapeutic interventions. Surprisingly, tolerance and reduced atherosclerotic burden were both dependent on the recently described IL-35 and not on IL-10, the immunosuppressive cytokine usually studied in the context of induced tolerance and amelioration of atherosclerotic symptoms. In addition to the above, using recombinant protein fragments, we were able to localize two epitopes of the α1(V) chain involved in col(V) autoimmunity in atherosclerotic Ldlr(-/-) mice, suggesting future courses of experimentation for the characterization of such epitopes.
Keywords: IL-35; atherosclerosis; autoimmune disease; autoimmunity; collagen type V; immunotherapy; vascular smooth muscle cells.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Type V collagen-induced nasal tolerance prevents lung damage in an experimental model: new evidence of autoimmunity to collagen V in COPD.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1444622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444622. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301030 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17-dependent autoimmunity to collagen type V in atherosclerosis.Circ Res. 2010 Oct 29;107(9):1106-16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.221069. Epub 2010 Sep 2. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20814021 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of oral tolerance to HSP60 or an HSP60-peptide activates T cell regulation and reduces atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007 Dec;27(12):2677-83. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.151274. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17901374
-
Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Immunomodulatory Therapy for Atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019 Aug;33(4):385-398. doi: 10.1007/s10557-019-06890-0. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019. PMID: 31332656
-
Autoimmune diseases and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Nov;21(11):780-807. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01045-7. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38937626 Review.
Cited by
-
Treg-Cell-Derived IL-35-Coated Extracellular Vesicles Promote Infectious Tolerance.Cell Rep. 2020 Jan 28;30(4):1039-1051.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.12.081. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 31995748 Free PMC article.
-
Type V collagen-induced nasal tolerance prevents lung damage in an experimental model: new evidence of autoimmunity to collagen V in COPD.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1444622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444622. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301030 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Autoimmunity to Peptides of Collagen V α1 Chain as Newly Biomarkers of Early Stage of Systemic Sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 12;11:604602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.604602. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33643291 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious Tolerance as Seen With 2020 Vision: The Role of IL-35 and Extracellular Vesicles.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 26;11:1867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01867. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th17 Responses to Collagen Type V, kα1-Tubulin, and Vimentin Are Present Early in Human Development and Persist Throughout Life.Am J Transplant. 2017 Apr;17(4):944-956. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14097. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Am J Transplant. 2017. PMID: 27801552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ketelhuth D. F., and Hansson G. K. (2015) Modulation of autoimmunity and atherosclerosis: common targets and promising translational approaches against disease. Circ. J. 79, 924–933 - PubMed
-
- Ketelhuth D. F., Gisterå A., Johansson D. K., and Hansson G. K. (2013) T cell-based therapies for atherosclerosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 19, 5850–5858 - PubMed
-
- Zhou X., Robertson A. K., Hjerpe C., and Hansson G. K. (2006) Adoptive transfer of CD4+ T cells reactive to modified low-density lipoprotein aggravates atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 26, 864–870 - PubMed
-
- Blasi C. (2008) The autoimmune origin of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 201, 17–32 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

