Plasma concentrations of adrenomedullin and atrial and brain natriuretic peptides in patients with adrenal pheochromocytoma
- PMID: 26722306
- PMCID: PMC4665925
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3660
Plasma concentrations of adrenomedullin and atrial and brain natriuretic peptides in patients with adrenal pheochromocytoma
Abstract
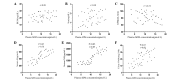
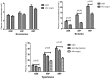
The present study aimed to evaluate any changes in the plasma concentrations of adrenomedullin (ADM), atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) in patients with adrenal pheochromocytoma (PC). The plasma concentrations of the three peptides were measured in 45 healthy control individuals and 90 untreated patients with PC, who consisted of 20 normotensive patients, 30 borderline hypertensive patients and 40 hypertensive patients. After 4 weeks of effective antihypertensive therapy for hypertensive PC patients, the concentrations of ADM, ANP and BNP were measured again, and laparoscopic adrenalectomy was then performed for all PC patients with values that were measured 2 weeks later. The plasma concentrations of the three peptides were significantly increased in the borderline hypertensive and hypertensive patients compared with the concentrations in control individuals and normotensive patients. In addition, there were significant differences between the levels of ADM, ANP and BNP in the borderline and hypertensive groups. The plasma ADM concentration was not associated with the blood urea nitrogen levels, serum creatinine levels or glomerular filtration rate, but was correlated with the serum epinephrine, serum norepinephrine and urine vanillylmandelic acid levels. In addition, the ADM concentration was associated with the systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, left ventricular ejection fraction, left ventricular mass index and plasma concentrations of ANP and BNP in the hypertensive patients with PC. After 4 weeks of antihypertensive treatment, the values of the three peptides in the hypertensive patients with PC were not significantly changed. As expected, the values in borderline and hypertensive groups were significantly decreased 2 weeks subsequent to surgery, whereas there were no significant changes in the normotensive group. ADM may participate, along with ANP and BNP, in the mechanisms that counteract further elevation of blood pressure in patients with PC, and there may be an ADM/catecholamine local regulatory mechanism that is important for the control of adrenal medulla functions.
Keywords: adrenal; adrenomedullin; atrial natriuretic peptide; brain natriuretic peptide; pheochromocytoma.
Figures
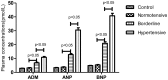

Similar articles
-
Changes of adrenomedullin and natriuretic peptides in patients with adrenal medullary hyperplasia prior to and following pharmacological therapy and adrenalectomy.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Aug;12(2):864-872. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3418. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27446289 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological functions of adrenomedullin and natriuretic peptides in patients with primary aldosteronism.Endocrine. 2015 Mar;48(2):661-8. doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0316-9. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Endocrine. 2015. PMID: 25027294
-
Plasma concentrations of adrenomedullin and natriuretic peptides in patients with essential hypertension.Exp Ther Med. 2015 May;9(5):1901-1908. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2345. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26136912 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of cardiac adrenomedullin and natriuretic peptide gene expression by AT1 receptor antagonism and ACE inhibition in normotensive and hypertensive rats.J Hypertens. 1999 Nov;17(11):1543-52. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199917110-00006. J Hypertens. 1999. PMID: 10608466
-
Adrenomedullin and diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2014 Jun 15;5(3):364-71. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i3.364. World J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24936257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor metabolism in pheochromocytomas: clinical and therapeutic implications.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5(2):349-373. doi: 10.37349/etat.2024.00222. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024. PMID: 38745767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertension and cardiac damage in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma patients: a large-scale single-center cohort study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jun 26;24(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03936-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38926862 Free PMC article.
-
Intricacies of the Molecular Machinery of Catecholamine Biosynthesis and Secretion by Chromaffin Cells of the Normal Adrenal Medulla and in Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 6;11(8):1121. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081121. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31390824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patients with pheochromocytoma exhibit low aldosterone renin ratio-preliminary reports.BMC Endocr Disord. 2020 Sep 11;20(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-00620-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020. PMID: 32917197 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
