Prognostic significance of CXCL12, CXCR4, and CXCR7 in patients with breast cancer
- PMID: 26722521
- PMCID: PMC4680466
Prognostic significance of CXCL12, CXCR4, and CXCR7 in patients with breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 play important roles in cancer invasion and metastasis. This study investigated the mRNA expressions of CXCL12, CXCR4, and CXCR7 to illustrate the role of these biomarkers in breast cancer metastasis and prognosis.
Methods: The mRNA expressions of CXCL12, CXCR4, and CXCR7 in 115 primary breast cancer and regional lymph node specimens were detected by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Survival time was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier survival curves using log-rank test. Univariable and multivariable Cox regression analyses were performed to assess independent prognostic factors for survival.
Results: The expression levels of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in breast cancer tissues were significantly higher than that in adjacent normal tissues (P=0.022 and P<0.001, respectively), while the expression level of CXCL12 in breast cancer tissues did not differ from that in adjacent normal tissues (P=0.156). Furthermore, CXCL12 exhibited significant differences in expression between primary tumor and lymph node metastasis tumor (P=0.039). CXCR4 and CXCR7 expressions in metastasis tumor were also higher, although no significant difference was observed (P=0.067 and P=0.054, respectively). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed that patients exhibiting high CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression experienced a shorter survival period compared with those with low expression. When analyzed with a Cox regression model, the expressions of CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 were independent prognostic factors for overall survival.
Conclusions: The mRNA expressions of CXCL12, CXCR4, and CXCR7 play important roles in the progression and metastasis of breast cancer and may act as predictive factors significantly affecting the prognosis.
Keywords: CXCL12; CXCR4; CXCR7; breast cancer; prognosis.
Figures
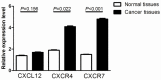

Similar articles
-
Inflammatory CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis mediates G-protein signaling pathway to influence the invasion and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):8169-79. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4686-2. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26715277
-
Correlation between CXCR4/CXCR7/CXCL12 chemokine axis expression and prognosis in lymph-node-positive lung cancer patients.Cancer Sci. 2018 Jan;109(1):154-165. doi: 10.1111/cas.13422. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29032612 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenging of CXCL12 by CXCR7 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of CXCR4-positive breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2012 Nov 8;31(45):4750-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.633. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22266857 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine receptors CXCR4/CXCR7 and their primary heterodimeric ligands CXCL12 and CXCL12/high mobility group box 1 in pancreatic cancer growth and development: finding flow.Pancreas. 2015 May;44(4):528-34. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000298. Pancreas. 2015. PMID: 25872129 Review.
-
Biological/pathological functions of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axes in the pathogenesis of bladder cancer.Int J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;22(6):991-1000. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1187-x. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29022185 Review.
Cited by
-
High ratio of pCXCR4/CXCR4 tumor infiltrating immune cells in primary high grade ovarian cancer is indicative for response to chemotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2022 Apr 9;22(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09374-x. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35397601 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous and Therapeutic Estrogens: Maestro Conductors of the Microenvironment of ER+ Breast Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 24;13(15):3725. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153725. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast Cancer: An Examination of the Potential of ACKR3 to Modify the Response of CXCR4 to CXCL12.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 14;19(11):3592. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113592. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30441765 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular subtypes predict the preferential site of distant metastasis in advanced breast cancer: a nationwide retrospective study.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 25;13:978985. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.978985. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36761968 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of CXCR4 and CXCR7 knockout by CRISPR/Cas9 on the function of triple-negative breast cancer cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 17;12:3849-3858. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S195661. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31190884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:591–602. - PubMed
-
- Müller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, Barrera JL, Mohar A, Verástegui E, Zlotnik A. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50–56. - PubMed
-
- Paget S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989;8:98–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
