Transcutaneous Cervical Vagus Nerve Stimulation Ameliorates Acute Ischemic Injury in Rats
- PMID: 26723020
- PMCID: PMC4789082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2015.11.008
Transcutaneous Cervical Vagus Nerve Stimulation Ameliorates Acute Ischemic Injury in Rats
Abstract
Background: Direct stimulation of the vagus nerve in the neck via surgically implanted electrodes is protective in animal models of stroke. We sought to determine the safety and efficacy of a non-invasive cervical VNS (nVNS) method using surface electrodes applied to the skin overlying the vagus nerve in the neck in a model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO).
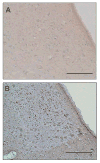
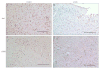
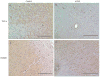
Methods: nVNS was initiated variable times after MCAO in rats (n = 33). Control animals received sham stimulation (n = 33). Infarct volume and functional outcome were assessed on day 7. Brains were processed by immunohistochemistry for microglial activation and cytokine levels. The ability of nVNS to activate the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) was assessed using c-Fos immunohistochemistry.
Results: Infarct volume was 43.15 ± 3.36 percent of the contralateral hemisphere (PCH) in control and 28.75 ± 4.22 PCH in nVNS-treated animals (p < 0.05). The effect of nVNS on infarct size was consistent when stimulation was initiated up to 4 hours after MCAO. There was no difference in heart rate and blood pressure between control and nVNS-treated animals. The number of c-Fos positive cells was 32.4 ± 10.6 and 6.2 ± 6.3 in the ipsilateral NTS (p < 0.05) and 30.4 ± 11.2 and 5.8 ± 4.3 in the contralateral NTS (p < 0.05) in nVNS-treated and control animals, respectively. nVNS reduced the number of Iba-1, CD68, and TNF-α positive cells and increased the number of HMGB1 positive cells.
Conclusions: nVNS inhibits ischemia-induced immune activation and reduces the extent of tissue injury and functional deficit in rats without causing cardiac or hemodynamic adverse effects when initiated up to 4 hours after MCAO.
Keywords: Cerebral ischemia; Electrical stimulation; Inflammation; Neuroprotection; Vagus nerve.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Reis DJ, Berger SB, Underwood MD, Khayata M. Electrical stimulation of cerebellar fastigial nucleus reduces ischemic infarction elicited by middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991;11:810–8. - PubMed
-
- Glickstein SB, Ilch CP, Golanov EV. Electrical stimulation of the dorsal periaqueductal gray decreases volume of the brain infarction independently of accompanying hypertension and cerebrovasodilation. Brain Res. 2003;994:135–45. - PubMed
-
- Glickstein SB, Ilch CP, Reis DJ, Golanov EV. Stimulation of the subthalamic vasodilator area and fastigial nucleus independently protects the brain against focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2001;912:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Henninger N, Fisher M. Stimulating circle of Willis nerve fibers preserves the diffusion-perfusion mismatch in experimental stroke. Stroke. 2007;38:2779–86. - PubMed
-
- Ay I, Lu J, Ay H, Gregory Sorensen A. Vagus nerve stimulation reduces infarct size in rat focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2009;459:147–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

