A continuous spectrophotometric enzyme-coupled assay for deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolases
- PMID: 26723493
- PMCID: PMC4744544
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2015.11.027
A continuous spectrophotometric enzyme-coupled assay for deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolases
Abstract
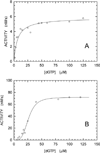
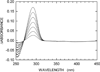
We describe a continuous, spectrophotometric, enzyme-coupled assay useful to monitor reactions catalyzed by nucleoside triphosphohydrolases. In particular, using Escherichia coli deoxynucleoside triphosphohydrolase (Dgt), which hydrolyzes dGTP to deoxyguanosine and tripolyphosphate (PPPi) as the enzyme to be tested, we devised a procedure relying on purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNPase) and xanthine oxidase (XOD) as the auxiliary enzymes. The deoxyguanosine released by Dgt can indeed be conveniently subjected to phosphorolysis by PNPase, yielding deoxyribose-1-phosphate and guanine, which in turn can be oxidized to 8-oxoguanine by XOD. By this means, it was possible to continuously detect Dgt activity at 297 nm, at which wavelength the difference between the molar extinction coefficients of 8-oxoguanine (8000 M(-1) cm(-1)) and guanine (1090 M(-1) cm(-1)) is maximal. The initial velocities of Dgt-catalyzed reactions were then determined in parallel with the enzyme-coupled assay and with a discontinuous high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method able to selectively detect deoxyguanosine. Under appropriate conditions of excess auxiliary enzymes, the activities determined with our continuous enzyme-coupled assay were quantitatively comparable to those observed with the HPLC method. Moreover, the enzyme-coupled assay proved to be more sensitive than the chromatographic procedure, permitting reliable detection of Dgt activity at low dGTP substrate concentrations.
Keywords: 8-Oxoguanine; Deoxynucleoside triphosphatase; Enzyme-coupled assay; Escherichia coli Dgt; Purine nucleoside phosphorylase; Xanthine oxidase.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Lascu I, Gonin P. The catalytic mechanism of nucleoside diphosphate kinases. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2000;32:237–246. - PubMed
-
- Lascu L, Giartosio A, Ransac S, Erent M. Quaternary structure of nucleoside diphosphate kinases. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2000;32:227–236. - PubMed
-
- Bernard MA, Ray NB, Olcott MC, Hendricks SP, Mathews CK. Metabolic functions of microbial nucleoside diphosphate kinases. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2000;32:259–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

