3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues
- PMID: 26724184
- PMCID: PMC4879088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.12.011
3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues
Abstract
Bioprinting is a 3D fabrication technology used to precisely dispense cell-laden biomaterials for the construction of complex 3D functional living tissues or artificial organs. While still in its early stages, bioprinting strategies have demonstrated their potential use in regenerative medicine to generate a variety of transplantable tissues, including skin, cartilage, and bone. However, current bioprinting approaches still have technical challenges in terms of high-resolution cell deposition, controlled cell distributions, vascularization, and innervation within complex 3D tissues. While no one-size-fits-all approach to bioprinting has emerged, it remains an on-demand, versatile fabrication technique that may address the growing organ shortage as well as provide a high-throughput method for cell patterning at the micrometer scale for broad biomedical engineering applications. In this review, we introduce the basic principles, materials, integration strategies and applications of bioprinting. We also discuss the recent developments, current challenges and future prospects of 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Combined with recent advances in human pluripotent stem cell technologies, 3D-bioprinted tissue models could serve as an enabling platform for high-throughput predictive drug screening and more effective regenerative therapies.
Keywords: 3D printing; Bioink; Bioprinting; Drug screening; Hydrogel; Regenerative medicine; Tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

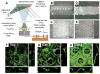

References
-
- Abouna GM. Organ Shortage Crisis: Problems and Possible Solutions. Transplant Proc. 2008;40(1):34–8. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, Greiner A, Wendorff JH. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog Polym Sci. 2013;38(6):963–91.
-
- Arai K, Iwanaga S, Toda H, Genci C, Nishiyama Y, Nakamura M. Three-dimensional inkjet biofabrication based on designed images. Biofabrication. 2011:034113. - PubMed
-
- Araujo JV, Davidenko N, Danner M, Cameron RE, Best SM. Novel porous scaffolds of pH responsive chitosan/carrageenan-based polyelectrolyte complexes for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res - Part A. 2014:4415–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

