TCA Cycle and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Are Necessary for Diverse Biological Functions
- PMID: 26725009
- PMCID: PMC4724312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.12.002
TCA Cycle and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Are Necessary for Diverse Biological Functions
Abstract
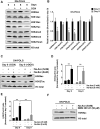
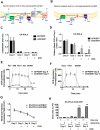
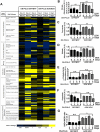
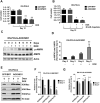
Mitochondrial metabolism is necessary for the maintenance of oxidative TCA cycle function and mitochondrial membrane potential. Previous attempts to decipher whether mitochondria are necessary for biological outcomes have been hampered by genetic and pharmacologic methods that simultaneously disrupt multiple functions linked to mitochondrial metabolism. Here, we report that inducible depletion of mitochondrial DNA (ρ(ο) cells) diminished respiration, oxidative TCA cycle function, and the mitochondrial membrane potential, resulting in diminished cell proliferation, hypoxic activation of HIF-1, and specific histone acetylation marks. Genetic reconstitution only of the oxidative TCA cycle function specifically in these inducible ρ(ο) cells restored metabolites, resulting in re-establishment of histone acetylation. In contrast, genetic reconstitution of the mitochondrial membrane potential restored ROS, which were necessary for hypoxic activation of HIF-1 and cell proliferation. These results indicate that distinct mitochondrial functions associated with respiration are necessary for cell proliferation, epigenetics, and HIF-1 activation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Appleby RD, Porteous WK, Hughes G, James AM, Shannon D, Wei YH, Murphy MP. Quantitation and origin of the mitochondrial membrane potential in human cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. European journal of biochemistry / FEBS. 1999;262:108–116. - PubMed
-
- Buchet K, Godinot C. Functional F1-ATPase essential in maintaining growth and membrane potential of human mitochondrial DNA-depleted rho degrees cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1998;273:22983–22989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL122062/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA157996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008061/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA12306708/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123067/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008152/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 T32HL076139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL076139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

