Long-Term ERK Inhibition in KRAS-Mutant Pancreatic Cancer Is Associated with MYC Degradation and Senescence-like Growth Suppression
- PMID: 26725216
- PMCID: PMC4816652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.11.011
Long-Term ERK Inhibition in KRAS-Mutant Pancreatic Cancer Is Associated with MYC Degradation and Senescence-like Growth Suppression
Abstract
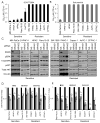
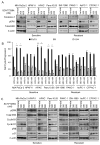
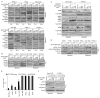
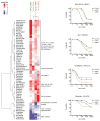
Induction of compensatory mechanisms and ERK reactivation has limited the effectiveness of Raf and MEK inhibitors in RAS-mutant cancers. We determined that direct pharmacologic inhibition of ERK suppressed the growth of a subset of KRAS-mutant pancreatic cancer cell lines and that concurrent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibition caused synergistic cell death. Additional combinations that enhanced ERK inhibitor action were also identified. Unexpectedly, long-term treatment of sensitive cell lines caused senescence, mediated in part by MYC degradation and p16 reactivation. Enhanced basal PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling was associated with de novo resistance to ERK inhibitor, as were other protein kinases identified by kinome-wide siRNA screening and a genetic gain-of-function screen. Our findings reveal distinct consequences of inhibiting this kinase cascade at the level of ERK.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
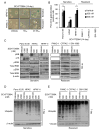


References
-
- Bonet C, Giuliano S, Ohanna M, Bille K, Allegra M, Lacour JP, Bahadoran P, Rocchi S, Ballotti R, Bertolotto C. Aurora B is regulated by the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) signaling pathway and is a valuable potential target in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:29887–29898. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

