The Lipid Bilayer Modulates the Structure and Function of an ATP-binding Cassette Exporter
- PMID: 26725230
- PMCID: PMC4813473
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.698498
The Lipid Bilayer Modulates the Structure and Function of an ATP-binding Cassette Exporter
Abstract
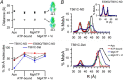
ATP-binding cassette exporters use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to transport substrates across membranes by switching between inward- and outward-facing conformations. Essentially all structural studies of these proteins have been performed with the proteins in detergent micelles, locked in specific conformations and/or at low temperature. Here, we used luminescence resonance energy transfer spectroscopy to study the prototypical ATP-binding cassette exporter MsbA reconstituted in nanodiscs at 37 °C while it performs ATP hydrolysis. We found major differences when comparing MsbA in these native-like conditions with double electron-electron resonance data and the crystal structure of MsbA in the open inward-facing conformation. The most striking differences include a significantly smaller separation between the nucleotide-binding domains and a larger fraction of molecules with associated nucleotide-binding domains in the nucleotide-free apo state. These studies stress the importance of studying membrane proteins in an environment that approaches physiological conditions.
Keywords: ABC transporter; FRET; LRET; MsbA; fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET); luminescence resonance energy transfer; membrane bilayer; multidrug transporter; nanodisc; spectroscopy.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


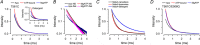
References
-
- Al-Shawi M. K. (2011) Catalytic and transport cycles of ABC exporters. Essays Biochem. 50, 63–83 - PubMed
-
- Bouige P., Laurent D., Piloyan L., and Dassa E. (2002) Phylogenetic and functional classification of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) systems. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 3, 541–559 - PubMed
-
- Sharom F. J. (2008) ABC multidrug transporters: structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics 9, 105–127 - PubMed
-
- Hopfner K. P., Karcher A., Shin D. S., Craig L., Arthur L. M., Carney J. P., and Tainer J. A. (2000) Structural biology of Rad50 ATPase: ATP-driven conformational control in DNA double-strand break repair and the ABC-ATPase superfamily. Cell 101, 789–800 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

