The functions of TRPP2 in the vascular system
- PMID: 26725733
- PMCID: PMC4722977
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2015.126
The functions of TRPP2 in the vascular system
Abstract
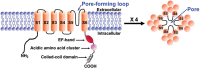
TRPP2 (polycystin-2, PC2 or PKD2), encoded by the PKD2 gene, is a non-selective cation channel with a large single channel conductance and high Ca(2+) permeability. In cell membrane, TRPP2, along with polycystin-1, TRPV4 and TRPC1, functions as a mechanotransduction channel. In the endoplasmic reticulum, TRPP2 modulates intracellular Ca(2+) release associated with IP3 receptors and the ryanodine receptors. Noteworthily, TRPP2 is widely expressed in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells of all major vascular beds, and contributes to the regulation of vessel function. The mutation of the PKD2 gene is a major cause of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is not only a common genetic disease of the kidney but also a systemic disorder associated with abnormalities in the vasculature; cardiovascular complications are the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in ADPKD patients. This review provides an overview of the current knowledge regarding the TRPP2 protein and its possible role in cardiovascular function and related diseases.
Figures
References
-
- 1Mochizuki T, Wu G, Hayashi T, Xenophontos SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, et al. PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science 1996; 272: 1339–42. - PubMed
-
- 2Delmas P, Padilla F, Osorio N, Coste B, Raoux M, Crest M. Polycystins, calcium signaling, and human diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 322: 1374–83. - PubMed
-
- 5Cai Y, Maeda Y, Cedzich A, Torres VE, Wu G, Hayashi T, et al. Identification and characterization of polycystin-2, the PKD2 gene product. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 2855765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

