Control of lysosomal biogenesis and Notch-dependent tissue patterning by components of the TFEB-V-ATPase axis in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 26727288
- PMCID: PMC4836007
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1134080
Control of lysosomal biogenesis and Notch-dependent tissue patterning by components of the TFEB-V-ATPase axis in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
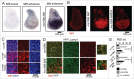
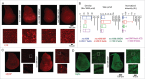
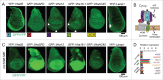
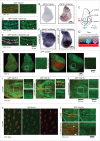
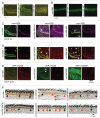
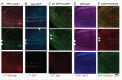
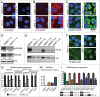
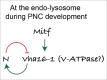
In vertebrates, TFEB (transcription factor EB) and MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor) family of basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factors regulates both lysosomal function and organ development. However, it is not clear whether these 2 processes are interconnected. Here, we show that Mitf, the single TFEB and MITF ortholog in Drosophila, controls expression of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase pump (V-ATPase) subunits. Remarkably, we also find that expression of Vha16-1 and Vha13, encoding 2 key components of V-ATPase, is patterned in the wing imaginal disc. In particular, Vha16-1 expression follows differentiation of proneural regions of the disc. These regions, which will form sensory organs in the adult, appear to possess a distinctive endolysosomal compartment and Notch (N) localization. Modulation of Mitf activity in the disc in vivo alters endolysosomal function and disrupts proneural patterning. Similar to our findings in Drosophila, in human breast epithelial cells we observe that impairment of the Vha16-1 human ortholog ATP6V0C changes the size and function of the endolysosomal compartment and that depletion of TFEB reduces ligand-independent N signaling activity. Our data suggest that lysosomal-associated functions regulated by the TFEB-V-ATPase axis might play a conserved role in shaping cell fate.
Keywords: Notch signaling; SOP; TFEB; V-ATPase; autophagy; lysosome; mitf; patterning.
Figures

References
-
- Forgac M. Vacuolar ATPases: rotary proton pumps in physiology and pathophysiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8:917-29; PMID:17912264; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrm2272 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hinton A, Bond S, Forgac M. V-ATPase functions in normal and disease processes. Pflugers Arch 2009; 457:589-98; PMID:18026982; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1007/s00424-007-0382-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buechling T, Bartscherer K, Ohkawara B, Chaudhary V, Spirohn K, Niehrs C, Boutros M. Wnt/Frizzled signaling requires dPRR, the Drosophila homolog of the prorenin receptor. Curr Biol 2010; 20:1263-8; PMID:20579883; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.cub.2010.05.028 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cruciat C-M, Ohkawara B, Acebron SP, Karaulanov E, Reinhard C, Ingelfinger D, Boutros M, Niehrs C. Requirement of prorenin receptor and vacuolar H+-ATPase-mediated acidification for Wnt signaling. Science 2010; 327:459-63; PMID:20093472; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1179802 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gleixner EM, Canaud G, Hermle T, Guida MC, Kretz O, Helmstädter M, Huber TB, Eimer S, Terzi F, Simons M. V-ATPase/mTOR signaling regulates megalin-mediated apical endocytosis. Cell Rep 2014; 8:10-9; PMID:24953654; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.035 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
