The Polymerase Activity of Mammalian DNA Pol ζ Is Specifically Required for Cell and Embryonic Viability
- PMID: 26727495
- PMCID: PMC4699697
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005759
The Polymerase Activity of Mammalian DNA Pol ζ Is Specifically Required for Cell and Embryonic Viability
Abstract
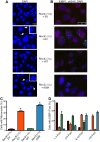
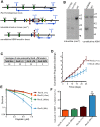
DNA polymerase ζ (pol ζ) is exceptionally important for maintaining genome stability. Inactivation of the Rev3l gene encoding the polymerase catalytic subunit causes a high frequency of chromosomal breaks, followed by lethality in mouse embryos and in primary cells. Yet it is not known whether the DNA polymerase activity of pol ζ is specifically essential, as the large REV3L protein also serves as a multiprotein scaffold for translesion DNA synthesis via multiple conserved structural domains. We report that Rev3l cDNA rescues the genomic instability and DNA damage sensitivity of Rev3l-null immortalized mouse fibroblast cell lines. A cDNA harboring mutations of conserved catalytic aspartate residues in the polymerase domain of REV3L could not rescue these phenotypes. To investigate the role of REV3L DNA polymerase activity in vivo, a Rev3l knock-in mouse was constructed with this polymerase-inactivating alteration. No homozygous mutant mice were produced, with lethality occurring during embryogenesis. Primary fibroblasts from mutant embryos showed growth defects, elevated DNA double-strand breaks and cisplatin sensitivity similar to Rev3l-null fibroblasts. We tested whether the severe Rev3l-/- phenotypes could be rescued by deletion of DNA polymerase η, as has been reported with chicken DT40 cells. However, Rev3l-/- Polh-/- mice were inviable, and derived primary fibroblasts were as sensitive to DNA damage as Rev3l-/- Polh+/+ fibroblasts. Therefore, the functions of REV3L in maintaining cell viability, embryonic viability and genomic stability are directly dependent on its polymerase activity, and cannot be ameliorated by an additional deletion of pol η. These results validate and encourage the approach of targeting the DNA polymerase activity of pol ζ to sensitize tumors to DNA damaging agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Shen X, Jun S, O'Neal LE, Sonoda E, Bemark M, Sale JE, et al. REV3 and REV1 play major roles in recombination-independent repair of DNA interstrand cross-links mediated by monoubiquitinated proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). J Biol Chem. 2006;281(20):13869–72. . - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto K, Cho Y, Yang IY, Akagi J, Ohashi E, Tateishi S, et al. The vital role of polymerase ζ and REV1 in mutagenic, but not correct, DNA synthesis across benzo[a]pyrene-dG and recruitment of polymerase ζ by REV1 to replication-stalled site. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(12):9613–22. 10.1074/jbc.M111.331728 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

