The Role of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase in Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Liver Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 26727596
- PMCID: PMC4699706
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146279
The Role of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase in Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Liver Carcinogenesis
Abstract
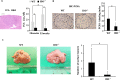
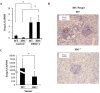
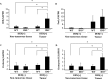
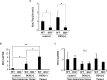
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), a tryptophan-catabolizing intracellular enzyme of the L-kynurenine pathway, causes preneoplastic cells and tumor cells to escape the immune system by inducing immune tolerance; this mechanism might be associated with the development and progression of human malignancies. In the present study, we investigated the role of IDO in diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced hepatocarcinogenesis by using IDO-knockout (KO) mice. To induce hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hepatic adenoma, and preneoplastic hepatocellular lesions termed foci of cellular alteration (FCA), male IDO-wild-type (WT) and IDO-KO mice with a C57BL/6J background received a single intraperitoneal injection of DEN at 2 weeks of age. The mice were sacrificed to evaluate the development of FCA and hepatocellular neoplasms. HCC overexpressed IDO and L-kynurenine compared to surrounding normal tissue in the DEN-treated IDO-WT mice. The number and cell proliferative activity of FCAs, and the incidence and multiplicity of HCC were significantly greater in the IDO-WT than in the IDO-KO mice. The expression levels of the IDO protein, of L-kynurenine, and of IFN-γ, COX-2, TNF-α, and Foxp3 mRNA were also significantly increased in the DEN-induced hepatic tumors that developed in the IDO-WT mice. The mRNA expression levels of CD8, perforin and granzyme B were markedly increased in hepatic tumors developed in IDO-KO mice. Moreover, Foxp3-positive inflammatory cells had infiltrated into the livers of DEN-treated IDO-WT mice, whereas fewer cells had infiltrated into the livers of IDO-KO mice. Induction of IDO and elevation of L-kynurenine might play a critical role in both the early and late phase of liver carcinogenesis. Our findings suggest that inhibition of IDO might offer a promising strategy for the prevention of liver cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Marotta F, Vangieri B, Cecere A, Gattoni A. The pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma is multifactorial event. Novel immunological treatment in prospect. Clin Ter. 2004;155(5):187–99. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

