Hydroxychloroquine Use Is Associated With Decreased Incident Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- PMID: 26727968
- PMCID: PMC4859400
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002867
Hydroxychloroquine Use Is Associated With Decreased Incident Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. This study is the first to report the association of hydroxychloroquine (an antirheumatic medication that has been associated with decreased risk of diabetes, a less atherogenic lipid profile, and antithrombotic properties) with CVD in RA.
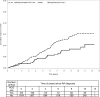
Methods and results: A retrospective incident RA cohort from January 1, 2001, to October 31, 2013, excluding patients with CVD prior to RA diagnosis, was constructed. Patients were categorized as hydroxychloroquine users versus nonusers and were allowed to contribute time to either group according to hydroxychloroquine exposure. The primary outcome was adjudicated incident CVD defined as a composite of coronary artery disease, stroke, transient ischemic attack, sudden cardiac death, and peripheral artery disease with arterial revascularization procedure. The secondary outcome was a composite of incident coronary artery disease, stroke, and transient ischemic attack. Cox time-varying regression models were used to estimate the association between hydroxychloroquine exposure and development of CVD, after adjusting for propensity score and relevant confounders, including demographics, CVD-related comorbidities, RA severity, and activity indicators and medications. We included 1266 RA patients, 547 hydroxychloroquine users, and 719 nonusers. During the observation period, 102 CVD events occurred, 3 in hydroxychloroquine users and 99 in nonusers. The fully adjusted Cox model showed a hazard ratio of 0.28 (95% CI 0.12-0.63, P=0.002) for incident CVD and 0.30 (95% CI 0.13-0.68, P=0.004) for incident composite coronary artery disease, stroke, and transient ischemic attack for hydroxychloroquine users versus nonusers, respectively.
Conclusion: In this hypothesis-generating study, hydroxychloroquine use was associated with a 72% decrease in the risk of incident CVD in RA patients. If these preliminary results are confirmed in larger studies, our findings may be used as a rationale for a randomized study of hydroxychloroquine use for primary prevention of CVD in RA or nonrheumatic high-risk patients.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; hydroxychloroquine; primary prevention; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
References
-
- Wolfe F, Mitchell DM, Sibley JT, Fries JF, Bloch DA, Williams CA, Spitz PW, Haga M, Kleinheksel SM, Cathey MA. The mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:481–494. - PubMed
-
- Avina‐Zubieta JA, Abrahamowicz M, De Vera MA, Choi HK, Sayre EC, Rahman MM, Sylvestre MP, Wynant W, Esdaile JM, Lacaille D. Immediate and past cumulative effects of oral glucocorticoids on the risk of acute myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis: a population‐based study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:68–75. - PubMed
-
- Solomon DH, Karlson EW, Rimm EB, Cannuscio CC, Mandl LA, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Curhan GC. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation. 2003;107:1303–1307. - PubMed
-
- del Rincon I, Freeman GL, Haas RW, O'Leary DH, Escalante A. Relative contribution of cardiovascular risk factors and rheumatoid arthritis clinical manifestations to atherosclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3413–3423. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical