Messenger RNA delivery of a cartilage-anabolic transcription factor as a disease-modifying strategy for osteoarthritis treatment
- PMID: 26728350
- PMCID: PMC4700530
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18743
Messenger RNA delivery of a cartilage-anabolic transcription factor as a disease-modifying strategy for osteoarthritis treatment
Abstract
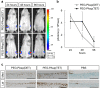
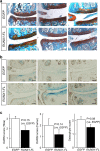
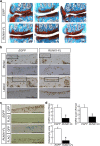
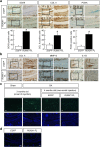
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic degenerative joint disease and a major health problem in the elderly population. No disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug (DMOAD) has been made available for clinical use. Here we present a disease-modifying strategy for OA, focusing on messenger RNA (mRNA) delivery of a therapeutic transcription factor using polyethylene glycol (PEG)-polyamino acid block copolymer-based polyplex nanomicelles. When polyplex nanomicelles carrying the cartilage-anabolic, runt-related transcription factor (RUNX) 1 mRNA were injected into mouse OA knee joints, OA progression was significantly suppressed compared with the non-treatment control. Expressions of cartilage-anabolic markers and proliferation were augmented in articular chondrocytes of the RUNX1-injected knees. Thus, this study provides a proof of concept of the treatment of degenerative diseases such as OA by the in situ mRNA delivery of therapeutic transcription factors; the presented approach will directly connect basic findings on disease-protective or tissue-regenerating factors to disease treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Hawker G. A. & Stanaitis I. Osteoarthritis year in review 2014: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 22, 1953–1957 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Felson D. T. et al. Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 133, 635–646 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Cross M. et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 1323–1330 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Arden N. & Nevitt M. C. Osteoarthritis: epidemiology. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 20, 3–25 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Reginster J. Y. & Khaltaev N. G. Introduction and WHO perspective on the global burden of musculoskeletal conditions. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41 Supp 1, 1–2 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

