Stepwise B-cell-dependent expansion of T helper clonotypes diversifies the T-cell response
- PMID: 26728651
- PMCID: PMC4728444
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10281
Stepwise B-cell-dependent expansion of T helper clonotypes diversifies the T-cell response
Abstract
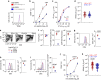
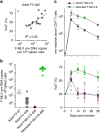
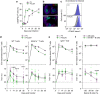
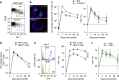
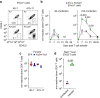
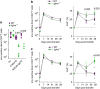
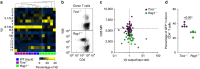
Antigen receptor diversity underpins adaptive immunity by providing the ground for clonal selection of lymphocytes with the appropriate antigen reactivity. Current models attribute T cell clonal selection during the immune response to T-cell receptor (TCR) affinity for either foreign or self peptides. Here, we report that clonal selection of CD4(+) T cells is also extrinsically regulated by B cells. In response to viral infection, the antigen-specific TCR repertoire is progressively diversified by staggered clonotypic expansion, according to functional avidity, which correlates with self-reactivity. Clonal expansion of lower-avidity T-cell clonotypes depends on availability of MHC II-expressing B cells, in turn influenced by B-cell activation. B cells clonotypically diversify the CD4(+) T-cell response also to vaccination or tumour challenge, revealing a common effect.
Figures

References
-
- Turner S. J., Doherty P. C., McCluskey J. & Rossjohn J. Structural determinants of T-cell receptor bias in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 883–894 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Thorborn G., Young G. R. & Kassiotis G. Effective T helper cell responses against retroviruses: are all clonotypes equal? J. Leukoc. Biol. 96, 27–37 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Morris G. P. & Allen P. M. How the TCR balances sensitivity and specificity for the recognition of self and pathogens. Nat. Immunol. 13, 121–128 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Gett A. V., Sallusto F., Lanzavecchia A. & Geginat J. T cell fitness determined by signal strength. Nat. Immunol. 4, 355–360 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

