PML isoform II plays a critical role in nuclear lipid droplet formation
- PMID: 26728854
- PMCID: PMC4700481
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201507122
PML isoform II plays a critical role in nuclear lipid droplet formation
Abstract
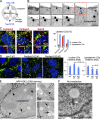
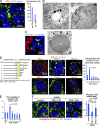
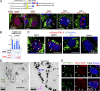
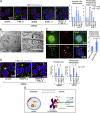
Lipid droplets (LDs) in the nucleus of hepatocyte-derived cell lines were found to be associated with premyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies (NBs) and type I nucleoplasmic reticulum (NR) or the extension of the inner nuclear membrane. Knockdown of PML isoform II (PML-II) caused a significant decrease in both nuclear LDs and type I NR, whereas overexpression of PML-II increased both. Notably, these effects were evident only in limited types of cells, in which a moderate number of nuclear LDs exist intrinsically, and PML-II was targeted not only at PML NBs, but also at the nuclear envelope, excluding lamins and SUN proteins. Knockdown of SUN proteins induced a significant increase in the type I NR and nuclear LDs, but these effects were cancelled by simultaneous knockdown of PML-II. Nuclear LDs harbored diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 and CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase α and incorporated newly synthesized lipid esters. These results corroborated that PML-II plays a critical role in generating nuclear LDs in specific cell types.
© 2016 Ohsaki et al.
Figures
Comment in
-
Lipid droplets go nuclear.J Cell Biol. 2016 Jan 4;212(1):7-8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201512056. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26728852 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

