Astaxanthin, a Carotenoid, Stimulates Immune Responses by Enhancing IFN-γ and IL-2 Secretion in Primary Cultured Lymphocytes in Vitro and ex Vivo
- PMID: 26729100
- PMCID: PMC4730289
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17010044
Astaxanthin, a Carotenoid, Stimulates Immune Responses by Enhancing IFN-γ and IL-2 Secretion in Primary Cultured Lymphocytes in Vitro and ex Vivo
Abstract
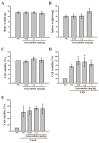
Astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant carotenoid, plays a major role in modulating the immune response. In this study, we examined the immunomodulatory effects of astaxanthin on cytokine production in primary cultured lymphocytes both in vitro and ex vivo. Direct administration of astaxanthin (70-300 nM) did not produce cytotoxicity in lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 µg/ mL)- or concanavalin A (Con A, 10 µg/ mL)-activated lymphocytes, whereas astaxanthin alone at 300 nM induced proliferation of splenic lymphocytes (p < 0.05) in vitro. Although astaxanthin, alone or with Con A, had no apparent effect on interferon (INF-γ) and interleukin (IL-2) production in primary cultured lymphocytes, it enhanced LPS-induced INF-γ production. In an ex vivo experiment, oral administration of astaxanthin (0.28, 1.4 and 7 mg/kg/day) for 14 days did not cause alterations in the body or spleen weights of mice and also was not toxic to lymphocyte cells derived from the mice. Moreover, treatment with astaxanthin significantly increased LPS-induced lymphocyte proliferation ex vivo but not Con A-stimulated lymphocyte proliferation ex vivo. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis revealed that administration of astaxanthin significantly enhanced INF-γ production in response to both LPS and Con A stimulation, whereas IL-2 production increased only in response to Con A stimulation. Also, astaxanthin treatment alone significantly increased IL-2 production in lymphocytes derived from mice, but did not significantly change production of INF-γ. These findings suggest that astaxanthin modulates lymphocytic immune responses in vitro, and that it partly exerts its ex vivo immunomodulatory effects by increasing INF-γ and IL-2 production without inducing cytotoxicity.
Keywords: Con A; IL-2; INF-γ; LPS; astaxanthin; immunomodulation; lymphocytes; mice.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Capsicum ethanol extracts and capsaicin enhance interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma production in cultured murine Peyer's patch cells ex vivo.Life Sci. 2007 Apr 3;80(17):1553-63. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.01.031. Epub 2007 Jan 27. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17306834
-
Cissampelos sympodialis Eichl. leaf extract increases the production of IL-10 by concanavalin-A-treated BALB/c spleen cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 1999 Oct;67(1):93-101. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(98)00235-9. J Ethnopharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10616965
-
Effects of boar seminal immunosuppressive fraction on production of cytokines by Concanavalin A-stimulated spleen cells and on proliferation of B lymphoma cell lines.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2003 Apr;49(4):249-54. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0897.2003.01221.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12852499
-
Roles of gamma interferon and other cytokines in suppression of the spleen cell proliferative response to concanavalin A and toxoplasma antigen during acute toxoplasmosis.Infect Immun. 1995 Mar;63(3):751-6. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.3.751-756.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7868243 Free PMC article.
-
The liquid culture filtrates of Paecilomyces tenuipes (Peck) Samson (=Isaria japonica Yasuda) and Paecilomyces cicadae (Miquel) Samson (=Isaria sinclairii (Berk.) Llond) regulate Th1 and Th2 cytokine response in murine Peyer's patch cells in vitro and ex vivo.Int Immunopharmacol. 2005 May;5(5):903-16. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2005.01.005. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15778126
Cited by
-
The Regulatory Roles of Toll-Like Receptor 4 in Secretions of Type 1/Type 2 Relative Cytokines by Splenocytes and Dendritic Cells Exposed to Clonorchis sinensis Excretory/Secretory Products.Inflammation. 2018 Feb;41(1):213-220. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0679-1. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29047038
-
Sex differences of inflammation in target organs, induced by intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide, depend on its dose.J Inflamm Res. 2018 Nov 8;11:431-445. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S178288. eCollection 2018. J Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 30519071 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances and the Mechanism of Astaxanthin in Ophthalmological Diseases.J Ophthalmol. 2022 May 20;2022:8071406. doi: 10.1155/2022/8071406. eCollection 2022. J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35646393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astaxanthin in Skin Health, Repair, and Disease: A Comprehensive Review.Nutrients. 2018 Apr 22;10(4):522. doi: 10.3390/nu10040522. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29690549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic immunomodulatory effect of eugenol and astaxanthin on doxorubicin cytotoxicity in hormonal positive breast Cancer cells.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Jan 28;22(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40360-021-00473-2. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33509300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mandal S.C., Lakshmi S.M. Pharmacognosy and phytotherapy research. In: Dwivedi P.K., Dwivedi S.K., editors. Biodiversity and Environmental Biotechnology. Scientific Publishers; Jodhpur, India: 2007. pp. 177–224.
-
- Bocci V., Paulesu L., Pessina G.P., Nicoletti C. The physiological interferon response. IX. Interferon activity in rabbit lymph after intraduodenal administration of alimentary lectins. Lymphokine Res. 1988;7:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Requena P., González R., López-Posadas R., Abadía-Molina A., Suárez M.D., Zarzuelo A., de Medina F.S., Martínez-Augustin O. The intestinal antiinflammatory agent glycomacropeptide has immunomodulatory actions on rat splenocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010;79:1797–1804. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.02.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

