Development of Novel Vaccines against Enterovirus-71
- PMID: 26729152
- PMCID: PMC4728561
- DOI: 10.3390/v8010001
Development of Novel Vaccines against Enterovirus-71
Abstract
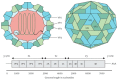
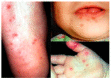
The hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by a group of Enteroviruses such as Enterovirus 71 (EV-A71) and Coxsackievirus CV-A5, CV-A8, and CV-A16. Mild symptoms of EV-A71 infection in children range from high fever, vomiting, rashes and ulcers in mouth but can produce more severe symptoms such as brainstem and cerebellar encephalitis, leading up to cardiopulmonary failure and death. The lack of vaccines and antiviral drugs against EV-A71 highlights the urgency of developing preventive and treatment agents against EV-A71 to prevent further fatalities. Research groups have developed experimental inactivated vaccines, recombinant Viral Protein 1 (VP1) vaccine and virus-like particles (VLPs). The inactivated EV-A71 vaccine is considered the safest viral vaccine, as there will be no reversion to the infectious wild type strain. The recombinant VP1 vaccine is a cost-effective immunogen, while VLPs contain an arrangement of epitopes that can elicit neutralizing antibodies against the virus. As each type of vaccine has its advantages and disadvantages, increased studies are required in the development of such vaccines, whereby high efficacy, long-lasting immunity, minimal risk to those vaccinated, safe and easy production, low cost, dispensing the need for refrigeration and convenient delivery are the major goals in their design.
Keywords: Enterovirus 71; foot and mouth disease; hand; inactivated vaccine; viral like particles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EV-A71 vaccine licensure: a first step for multivalent enterovirus vaccine to control HFMD and other severe diseases.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016 Jul 20;5(7):e75. doi: 10.1038/emi.2016.73. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 27436364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is a multivalent hand, foot, and mouth disease vaccine feasible?Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(11):2688-704. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1049780. Epub 2015 May 26. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 26009802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent development of enterovirus A vaccine candidates for the prevention of hand, foot, and mouth disease.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018 Sep;17(9):819-831. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2018.1510326. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018. PMID: 30095317 Review.
-
Novel recombinant chimeric virus-like particle is immunogenic and protective against both enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 in mice.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 19;5:7878. doi: 10.1038/srep07878. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25597595 Free PMC article.
-
A novel inactivated enterovirus 71 vaccine can elicit cross-protective immunity against coxsackievirus A16 in mice.Vaccine. 2016 Nov 21;34(48):5938-5945. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.10.018. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27771182
Cited by
-
ATP1B3: a virus-induced host factor against EV71 replication by up-regulating the production of type-I interferons.Virology. 2016 Sep;496:28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.05.013. Epub 2016 May 27. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27240146 Free PMC article.
-
Different responses of weather factors on hand, foot and mouth disease in three different climate areas of Gansu, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 8;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2860-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29310596 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Nanobiomaterials: Vaccines, Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases.Molecules. 2016 Jul 1;21(7):867. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070867. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27376260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin inhibited LPS-induced cytokine storm by interacting with the AKT1-FoxO1 and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in macrophages.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 8;14(1):20913. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71569-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39245773 Free PMC article.
-
Synergetic association between coxsackievirus A16 genotype evolution and recombinant form shifts.Virus Evol. 2023 Dec 20;10(1):vead080. doi: 10.1093/ve/vead080. eCollection 2024. Virus Evol. 2023. PMID: 38361814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pallansch M.A., Oberste M.S., Whitton J.L. Enteroviruses: Polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses and newer enteroviruses. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., Cohen J.I., Griffin D.E., Lamb R.A., Martin M.A., Racaniello V.R., Roizman B., editors. Fields Virology. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2003. pp. 490–530.
-
- Liu S.L., Pan H., Liu P., Amer S., Chan T.C., Zhan J., Huo X., Liu Y., Teng Z., Wang L., Zhuang H. Comparative epidemiology and virology of fatal and nonfatal cases of hand, foot and mouth disease in mainland China from 2008 to 2014. Rev. Med. Virol. 2015;25:115–28. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1827. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

