Pathogenesis of Type 2 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Renal and Hepatic Fibrosis
- PMID: 26729181
- PMCID: PMC4730129
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm5010004
Pathogenesis of Type 2 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Renal and Hepatic Fibrosis
Abstract
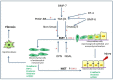
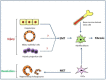
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), particularly, type 2 EMT, is important in progressive renal and hepatic fibrosis. In this process, incompletely regenerated renal epithelia lose their epithelial characteristics and gain migratory mesenchymal qualities as myofibroblasts. In hepatic fibrosis (importantly, cirrhosis), the process also occurs in injured hepatocytes and hepatic progenitor cells (HPCs), as well as ductular reaction-related bile epithelia. Interestingly, the ductular reaction contributes partly to hepatocarcinogenesis of HPCs, and further, regenerating cholangiocytes after injury may be derived from hepatic stellate cells via mesenchymal to epithelia transition, a reverse phenomenon of type 2 EMT. Possible pathogenesis of type 2 EMT and its differences between renal and hepatic fibrosis are reviewed based on our experimental data.
Keywords: animal models; bile ductular reaction; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; hepatic fibrosis; hepatic progenitor cells; myofibroblasts; renal fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study on the relationship between hepatic fibrosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110413. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110413. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32570119 Review.
-
Analysis of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-expressing ductular cells in a rat liver cirrhosis model induced by repeated injections of thioacetamide (TAA).Exp Mol Pathol. 2015 Jun;98(3):476-85. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25758201
-
Analysis of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in the histogenesis of hepatic progenitor cell in HBV-related liver diseases.Diagn Pathol. 2016 Nov 24;11(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0587-y. Diagn Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27881141 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of human amniotic epithelial cells on pro-fibrogenic resident hepatic cells in a rat model of liver fibrosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Feb;22(2):1202-1213. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13396. Epub 2017 Nov 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29105277 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Liver Fibrosis: Clues for a Better Understanding of the "Reactive" Biliary Epithelial Phenotype.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2953727. doi: 10.1155/2016/2953727. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 26880950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Insights into nickel-induced lung diseases.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Nov;76:99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.05.020. Epub 2021 May 29. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 34058338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Role for βA3/A1-Crystallin in Type 2 EMT of RPE Cells Occurring in Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Mar 20;59(4):AMD104-AMD113. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24132. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30098172 Free PMC article.
-
Oxalate induces type II epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in inner medullary collecting duct cells (IMCD) in vitro and stimulate the expression of osteogenic and fibrotic markers in kidney medulla in vivo.Oncotarget. 2019 Feb 1;10(10):1102-1118. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26634. eCollection 2019 Feb 1. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 30800221 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-Derived ADAM17 Promotes Liver Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 23;12:734351. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.734351. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34650435 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Augments Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 Induced Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in Lung Cell Culture Model.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020 Aug 25;19(4):348-361. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v19i4.4110. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33463102 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

