Morphine, a potential antagonist of cisplatin cytotoxicity, inhibits cisplatin-induced apoptosis and suppression of tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts
- PMID: 26729257
- PMCID: PMC4700493
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18706
Morphine, a potential antagonist of cisplatin cytotoxicity, inhibits cisplatin-induced apoptosis and suppression of tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts
Abstract
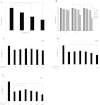
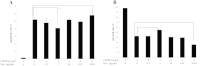
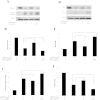
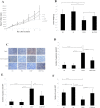
Morphine is an opioid analgesic drug often used for pain relief in cancer patients. However, there is growing evidence that morphine may modulate tumor growth, progression and metastasis. In this study, we evaluated whether morphine modulates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2 cells and whether morphine affects the antitumor activity of cisplatin on tumor growth in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2 xenografts in nude mice. We showed that a pretreatment with morphine (1 μg/ml) inhibited the sensitivity of CNE-2 cells to cisplatin by inhibiting cisplatin-induced CNE-2 cell apoptosis, decreasing caspase-3 activity and increasing the Bcl-2/Bax ratio. However, a high dose of morphine (1000 μg/ml) had the opposite effect. We also showed that at a low dose, morphine enhances chemoresistance in an in vivo nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) model by inhibiting cisplatin-induced apoptosis and decreasing neovascularization. Taken together, our results indicate that a low dose of morphine may lead to chemoresistance of cisplatin in NPC models in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting cisplatin-induced apoptosis and decreasing neovascularization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemosensitizing Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Inducing Apoptosis and Modulating Expression of Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio and Caspases.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Jan 26;23:462-469. doi: 10.12659/msm.903170. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28124680 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of tunicamycin combined with cisplatin on proliferation and apoptosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Jun;32(6):766-71. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22699051 Chinese.
-
Reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction is involved in apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE cells induced by Selaginella doederleinii extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Oct 31;138(1):184-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.072. Epub 2011 Sep 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21924341
-
The role of morphine in regulation of cancer cell growth.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;384(3):221-30. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0672-4. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21800094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of morphine in animal models of human cancer: does morphine promote or inhibit the tumor growth?Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:258141. doi: 10.1155/2013/258141. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24069592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA HIPK3: A Key Circular RNA in a Variety of Human Cancers.Front Oncol. 2020 May 15;10:773. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00773. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32500032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of the tumour suppressor κ-opioid receptor predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2017 Aug 18;17(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3541-9. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28821282 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine may act via DDX49 to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 5;13(9):12766-12779. doi: 10.18632/aging.202946. Epub 2021 May 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33952717 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt6 contributes tumorigenesis and development of colon cancer via its effects on cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell-cycle and migration.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):1163-1172. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8729. Epub 2018 May 16. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29963191 Free PMC article.
-
To Treat or Not to Treat: The Effects of Pain on Experimental Parameters.Comp Med. 2017 Dec 1;67(6):469-482. Comp Med. 2017. PMID: 29212578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McDermott A. L., Dutt S. N. & Watkinson J. C. The aetiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 26, 82–92 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Cheng S. H. et al. Concomitant radiotherapy and chemotherapy for early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 18, 2040–2045 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Serin M., Erkal H. S. & Cakmak A. Radiation therapy and concurrent cisplatin in management of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Acta Oncol 38, 1031–1035 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Epstein J. B. & Jones C. K. Presenting signs and symptoms of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 75, 32–36 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Huang H. Y., Wilkie D. J., Schubert M. M. & Ting L. L. Symptom profile of nasopharyngeal cancer patients during radiation therapy. Cancer Pract 8, 274–281 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

