Extracellular vesicles — new tool for joint repair and regeneration
- PMID: 26729461
- PMCID: PMC7116208
- DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.170
Extracellular vesicles — new tool for joint repair and regeneration
Abstract
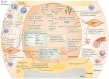
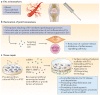
Cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs), present in synovial fluid and cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM), are involved in joint development and in the regulation of joint homeostasis. Although the exact function of EVs in these processes remains incompletely defined, the knowledge already acquired in this field suggests a role for these EVs as biomarkers of joint disease, and as a new tool to restore joint homeostasis and enhance articular tissue regeneration. In addition to direct injection of therapeutic EVs into the target site, surface coating of scaffolds and embedding of EVs in hydrogels might also lead to novel therapeutic possibilities. Based on the existing literature of EVs in synovial fluid and articular tissues, and investigation of the molecular factors (including microRNAs) active in joint homeostasis (or during its disturbance), we postulate novel perspectives for the implementation of EVs as a regenerative medicine approach in joint repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Berckmans RJ, et al. Cell-derived microparticles in synovial fluid from inflamed arthritic joints support coagulation exclusively via a factor VII-dependent mechanism. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:2857–2866. - PubMed
-
- Thery C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:569–579. - PubMed
-
- Thery C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:581–593. - PubMed
-
- Valadi H, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

