Clinical Spectrum of PRKAG2 Syndrome
- PMID: 26729852
- PMCID: PMC4704128
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCEP.115.003121
Clinical Spectrum of PRKAG2 Syndrome
Keywords: Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome; atrioventricular block; cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic; death, sudden, cardiac; defibrillators, implantable.
Figures
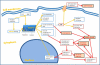
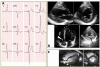
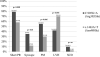
References
-
- Lev M, Leffler WB, Langendorf R, Pick A. Anatomic findings in a case of ventricular pre-excitation (WPW) terminating in complete atrioventricular block. Circulation. 1966;34:718–733. - PubMed
-
- Gulotta SJ, Gupta RD, Padmanabhan VT, Morrison J. Familial occurrence of sinus bradycardia, short PR interval, intraventricular conduction defects, recurrent supraventricular tachycardia, and cardiomegaly. Am Heart J. 1977;93:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Khair GZ, Soni JS, Bamrah VS. Syncope in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. II. Coexistence of atrioventricular block and wolff-parkinson-white syndrome. Am Heart J. 1985;110:1083–1086. - PubMed
-
- Gollob MH, Green MS, Tang AS, Gollob T, Karibe A, Ali Hassan AS, Ahmad F, Lozado R, Shah G, Fananapazir L, Bachinski LL, Roberts R. Identification of a gene responsible for familial wolff-parkinson-white syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1823–1831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

