Metabolic effects as a cause of myotoxic effects of fluoroquinolones
- PMID: 26729952
- PMCID: PMC4689014
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.169571
Metabolic effects as a cause of myotoxic effects of fluoroquinolones
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate if fluoroquinolones (FQs) influence skeletal muscle metabolism of healthy and malignant hyperthermia susceptible (MHS) pigs.
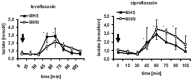
Materials and methods: After approval from of the Animal Care Committee, 10 MHS pigs, and 6 MHS pigs were anesthetized with hemodynamic and systemic metabolic monitoring. Microdialysis catheters were placed intramuscularly. After equilibration, levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin were injected as a rapid bolus and continuous infusions. Lactate was measured in the dialysate and statistically analyzed was done (Wilcoxon-test; U-test; P < 0.05).
Results: There were no differences in age, weight, and baseline lactate levels between the groups. Both applications of levofloxacin- and ciprofloxacin-induced an increase of local lactate levels in healthy and MHS pigs. No difference between the two groups was observed.
Conclusion: FQs influence skeletal muscle metabolism. Myotoxic effects of FQs can, therefore, be explained by an influence on the cellular energy balance.
Keywords: Fluoroquinolones; malignant hyperthermia; metabolism; myotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Bolon MK. The newer fluoroquinolones. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2009;23:1027–51. x. - PubMed
-
- Guis S, Bendahan D, Kozak-Ribbens G, Mattei JP, Le Fur Y, Confort-Gouny S, et al. Investigation of fluoroquinolone-induced myalgia using (31) P magnetic resonance spectroscopy and in vitro contracture tests. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:774–8. - PubMed
-
- Guis S, Jouglard J, Kozak-Ribbens G, Figarella-Branger D, Vanuxem D, Pellissier JF, et al. Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility revealed by myalgia and rhabdomyolysis during fluoroquinolone treatment. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:1405–6. - PubMed
-
- Petitjeans F, Nadaud J, Perez JP, Debien B, Olive F, Villevieille T, et al. A case of rhabdomyolysis with fatal outcome after a treatment with levofloxacin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;59:779–80. - PubMed
-
- Hsiao SH, Chang CM, Tsao CJ, Lee YY, Hsu MY, Wu TJ. Acute rhabdomyolysis associated with ofloxacin/levofloxacin therapy. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39:146–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical