Dendrimers as tunable vectors of drug delivery systems and biomedical and ocular applications
- PMID: 26730187
- PMCID: PMC4694674
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S93069
Dendrimers as tunable vectors of drug delivery systems and biomedical and ocular applications
Abstract
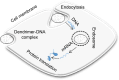
Dendrimers are large polymeric structures with nanosize dimensions (1-10 nm) and unique physicochemical properties. The major advantage of dendrimers compared with linear polymers is their spherical-shaped structure. During synthesis, the size and shape of the dendrimer can be customized and controlled, so the finished macromolecule will have a specific "architecture" and terminal groups. These characteristics will determine its suitability for drug delivery, diagnostic imaging, and as a genetic material carrier. This review will focus initially on the unique properties of dendrimers and their use in biomedical applications, as antibacterial, antitumor, and diagnostic agents. Subsequently, emphasis will be given to their use in drug delivery for ocular diseases.
Keywords: diagnostic agent; encapsulation; macromolecule; nanoparticles; ocular diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Kesharwani P, Jain K, Jain NK. Dendrimer as nanocarriers for drug delivery. Prog Polym Sci. 2014;39:268–307.
-
- Kannan RM, Nance E, Kannan S, Tomalia DA. Emerging concepts in dendrimer-based nanomedicine: from design principles to clinical applications. J Intern Med. 2014;276(6):579–617. - PubMed
-
- Tolia GT, Choi HH. The role of dendrimers in topical drug delivery. Pharm Technol. 2008;32(11):88–98.
-
- Semwal R, Semwal DK, Madan AK, Paul P, Mujaffer F, Badoni R. Dendrimers: a novel approach for drug targeting. J Pharm Res. 2010;3(9):2238–2247.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources