Do neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to the heightened risk of thrombosis in inflammatory diseases?
- PMID: 26730289
- PMCID: PMC4691810
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.829
Do neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to the heightened risk of thrombosis in inflammatory diseases?
Abstract
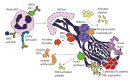
Thrombotic events, both arterial and venous, are a major health concern worldwide. Further, autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, and antiphospholipid syndrome, predispose to thrombosis, and thereby push the risk for these morbid events even higher. In recent years, neutrophils have been identified as important players in both arterial and venous thrombosis. Specifically, chromatin-based structures called neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) play a key role in activating the coagulation cascade, recruiting platelets, and serving as scaffolding upon which the thrombus can be assembled. At the same time, neutrophils and NETs are emerging as important mediators of pathogenic inflammation in the aforementioned autoimmune diseases. Here, we first review the general role of NETs in thrombosis. We then posit that exaggerated NET release contributes to the prothrombotic diatheses of systemic lupus erythematosus, ANCA-associated vasculitis, and antiphospholipid syndrome.
Keywords: Antiphospholipid syndrome; Lupus; Neutrophil extracellular traps; Thrombosis; Vasculitis.
Figures

References
-
- Silverstein MD, Heit JA, Mohr DN, Petterson TM, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ. Trends in the incidence of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a 25-year population-based study. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:585–593. - PubMed
-
- Naess IA, Christiansen SC, Romundstad P, Cannegieter SC, Rosendaal FR, Hammerstrøm J. Incidence and mortality of venous thrombosis: a population-based study. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:692–699. - PubMed
-
- Cohen AT, Tapson VF, Bergmann JF, Goldhaber SZ, Kakkar AK, Deslandes B, Huang W, Zayaruzny M, Emery L, Anderson FA. Venous thromboembolism risk and prophylaxis in the acute hospital care setting (ENDORSE study): a multinational cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2008;371:387–394. - PubMed
-
- Cushman M, Tsai AW, White RH, Heckbert SR, Rosamond WD, Enright P, Folsom AR. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in two cohorts: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology. Am J Med. 2004;117:19–25. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

