Statistical Evaluation of HTS Assays for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of β-Keto Esters
- PMID: 26730596
- PMCID: PMC4711668
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146104
Statistical Evaluation of HTS Assays for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of β-Keto Esters
Abstract
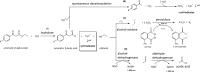
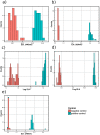
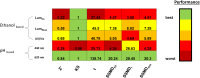
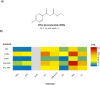
β-keto esters are used as precursors for the synthesis of β-amino acids, which are building blocks for some classes of pharmaceuticals. Here we describe the comparison of screening procedures for hydrolases to be used for the hydrolysis of β-keto esters, the first step in the preparation of β-amino acids. Two of the tested high throughput screening (HTS) assays depend on coupled enzymatic reactions which detect the alcohol released during ester hydrolysis by luminescence or absorption. The third assay detects the pH shift due to acid formation using an indicator dye. To choose the most efficient approach for screening, we assessed these assays with different statistical methods-namely, the classical Z'-factor, standardized mean difference (SSMD), the Kolmogorov-Smirnov-test, and t-statistics. This revealed that all three assays are suitable for HTS, the pH assay performing best. Based on our data we discuss the explanatory power of different statistical measures. Finally, we successfully employed the pH assay to identify a very fast hydrolase in an enzyme-substrate screening.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Liljeblad A, Kanerva LT. Biocatalysis as a profound tool in the preparation of highly enantiopure β-amino acids. Tetrahedron. 2006. June;62(25):5831–5854. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040402006005412. 10.1016/j.tet.2006.03.109 - DOI
-
- Umezawa H, Maeda K, Takeuchi T OY. New antibiotics, bleomycin A and B. The Journal of Antibiotics (Tokyo). 1966;19:200–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

