Epidural pain relief versus systemic opioid-based pain relief for abdominal aortic surgery
- PMID: 26731032
- PMCID: PMC6464571
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005059.pub4
Epidural pain relief versus systemic opioid-based pain relief for abdominal aortic surgery
Abstract
Background: Epidural analgesia offers greater pain relief compared to systemic opioid-based medications, but its effect on morbidity and mortality is unclear. This review was originally published in 2006 and was updated in 2012 and again in 2016.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of postoperative epidural analgesia in comparison with postoperative systemic opioid-based analgesia for adults undergoing elective abdominal aortic surgery.
Search methods: In the updated review, we searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE, and five trial registers in November 2014, together with reference checking to identify additional studies.
Selection criteria: We included all randomized controlled trials comparing postoperative epidural analgesia and postoperative systemic opioid-based analgesia for adults who underwent elective open abdominal aortic surgery.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information and data when required. We assessed the level of evidence according to the scale provided by the GRADE working group.
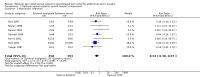
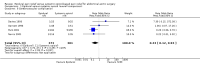
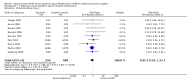
Main results: We included 15 trials published from 1987 to 2009 with 1498 participants in this updated review. Participants had a mean age between 60.5 and 71.3 years. The percentage of women in the included studies varied from 0% to 28.1%. Adding an epidural to general anaesthesia for people undergoing abdominal aortic repair reduced myocardial infarction (risk ratio (RR) 0.54 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.30 to 0.97); I(2) statistic = 0%; number needed to treat for one additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 28 (95% CI 19 to 1423), visual or verbal analogical scale (VAS) scores up to three days after the surgery (mean difference (MD) -1.78 (95% CI -2.32 to -1.25); I(2) statistic = 0% for VAS scores on movement at postoperative day one), time to tracheal extubation (standardized mean difference (SMD) -0.42 (95% CI -0.70 to -0.15); I(2) statistic = 83%; equivalent to a mean reduction of 36 hours), postoperative respiratory failure (RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.56 to 0.85); I(2) statistic = 0%; NNTB 8 (95% CI 6 to 16)), gastrointestinal bleeding (OR 0.20 (95% CI 0.06 to 0.65); I(2) statistic = 0%; NNTB 32 (95% CI 27 to 74)) and time spent in the intensive care unit (SMD -0.23 (95% CI -0.41 to -0.06); I(2) statistic = 0%; equivalent to a mean reduction of six hours). We did not demonstrate a reduction in the mortality rate up to 30 days (RR 1.06 (95% CI 0.60 to 1.86); I(2) statistic = 0%). The level of evidence was low for mortality and time before tracheal extubation; moderate for myocardial infarction, respiratory failure and intensive care unit length of stay; and high for gastrointestinal bleeding and VAS scores.
Authors' conclusions: Epidural analgesia provided better pain management, reduced myocardial infarction, time to tracheal extubation, postoperative respiratory failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, and intensive care unit length of stay compared with systemic opioid-based drugs. For mortality, we did not find a difference at 30 days.
Conflict of interest statement
Joanne Guay: I have had no direct relationship with any pharmaceutical company or equipment manufacturer in the past five years. I have not acted as witness expert in the past five years. I am not an author in any of the included or excluded studies. I do not hold any stock other than mutual funds. During the last five years, I have received fees as speaker for two lectures given at the University of Dalhousie: one on regional anaesthesia for carotid endarterectomy and the other on local anaesthetic‐related methaemoglobinaemia. My fees were paid by the University of Dalhousie. I am the editor of a multi authors textbook on anaesthesia (including notions on general and regional anaesthesia). I receive fees for a course on airway management at University of Quebec en Abitibi‐Temiscamingue.
Sandra Kopp: none known.
Figures



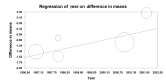

















Update of
-
Epidural pain relief versus systemic opioid-based pain relief for abdominal aortic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jul 11;(7):CD005059. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005059.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 05;(1):CD005059. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005059.pub4. PMID: 22786494 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Barre 1989 {published data only}
-
- Barre E, Raimbault E, Coriat P, Low Koune JP, Baron JF, Viars P. Monitoring of mixed venous oxygen saturation in aortic surgery: value and limits. Annales Francaises d'Anesthesie et de Reanimation 1989;8(6):688‐95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bois 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bois S, Couture P, Boudreault D, Lacombe P, Fuqure F, Girard D, et al. Epidural analgesia and intravenous patient‐controlled analgesia result in similar rates of postoperative myocardial ischemia after aortic surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1997;85(6):1233‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boylan 1998 {published data only}
-
- Boylan JF, Katz J, Kavanagh BP, Klinck JR, Cheng DC, DeMajo WC, et al. Epidural bupivacaine‐morphine analgesia versus patient‐controlled analgesia following abdominal aortic surgery: analgesic, respiratory, and myocardial effects. Anesthesiology 1998;89(3):585‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Broekema 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- Broekema AA, Veen A, Filder V, Gielen M, Hennis PJ. Postoperative analgesia with intramuscular morphine at fixed rate versus epidural morphine or sufentanil and bupivacaine in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1998;87(6):1346‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Davies 1993 {published data only}
-
- Davies MJ, Silbert BS, Mooney PJ, Dysart RH, Meads AC. Combined epidural and general anaesthesia versus general anaesthesia for abdominal aortic surgery: a prospective randomised trial. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 1993;21(6):790‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
de Lis 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lis AMS, Serrano MN, Alvarez MR, Pena JP, Gauna NM. Effects of postoperative pain on lung volume in patients undergoing aortic surgery. Revista Española de Anestesiología 1990;37(1):15‐8. [PUBMED: 2326519] - PubMed
Garnett 1996 {published data only}
-
- Garnett RL, MacIntyre A, Lindsay P, Barber GG, Cole CW, Hajjar G, et al. Perioperative ischaemia in aortic surgery: combined epidural/general anaesthesia and epidural analgesia vs general anaesthesia and iv analgesia. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 1996;43(8):769‐77. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kataja 1991 {published data only}
-
- Kataja J. Thoracolumbar epidural anaesthesia and isoflurane to prevent hypertension and tachycardia in patients undergoing abdominal aortic surgery. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 1991;8(6):427‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Muehling 2009 {published data only}
-
- Muehling B, Schelzig H, Steffen P, Meierhenrich R, Sunder‐Plassmann L, Orend KH. A prospective randomized trial comparing traditional and fast‐track patient care in elective open infrarenal aneurysm repair. World Journal of Surgery 2009;33(3):577‐85. [PUBMED: 19137363] - PubMed
-
- Muehling BM, Ortlieb L, Oberhuber A, Orend KH. Fast track management reduces the systemic inflammatory response and organ failure following elective infrarenal aortic aneurysm repair. Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 2011;12(5):784‐8. [PUBMED: 21343153] - PubMed
Norman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Norman JG, Fink GW, Strodel WE, Shawary P. The effects of epidural anaesthesia on the neuroendocrine response to major surgical stress: a randomized prospective trial. American Surgeon 1997;63(1):75‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Norris 2001 {published data only}
-
- Norris EJ, Beattie C, Perler BA, Martinez EA, Meinert CL, Anderson GF, et al. Double‐masked randomized trial comparing alternate combinations of intraoperative anaesthesia and postoperative analgesia in abdominal aortic surgery. Anesthesiology 2001;95(5):1054‐67. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Park 2001 {published and unpublished data}
Peyton 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Peyton PJ, Myles PS, Silbert BS, Rigg JA, Jamrozik K, Parsons R. Perioperative epidural analgesia and outcome after major abdominal surgery in high‐risk patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2003;96(2):548‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rigg JR, Jamrozik K, Myles PS, Silbert B, Peyton P, Parsons R, et al. Design of the multicenter Australian study of epidural anaesthesia and analgesia in major surgery: the MASTER trial. Controlled Clinical Trial 2000;21:244‐56. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rigg JR, Jamrozik K, Myles PS, Silbert BS, Peyton PJ, Parsons RW, et al. Epidural anaesthesia and analgesia and outcome of major surgery: a randomised trial. Lancet 2002;359:1276‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Reinhart 1989 {published data only}
-
- Reinhart K, Foehring U, Kersting T, Shaefer M, Bredle D, Hirner A, et al. Effects of thoracic epidural anaesthesia on systemic haemodynamic function and systemic oxygen supply‐demand relationship. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1989;69(3):360‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Stelzner J, Reinhart K, Fohring U, Henneberg M, Schafer M, Fitzner R. The effect of thoracic peridural analgesia on the cortisol and glucose response in surgery of the abdominal aorta. Regional Anaesthesie 1988;11(1):16‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yeager 1987 {published data only}
-
- Yeager MP, Glass DD, Neff RK, Brinck‐Johnsen T. Epidural anaesthesia and analgesia in high‐risk surgical patients. Anesthesiology 1987;66(6):729‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ahn 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ahn JH, Ahn HJ. Effect of thoracic epidural analgesia on recovery of bowel function after major upper abdominal surgery. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2016;34:247‐52. [PUBMED: 27687384] - PubMed
Akarsu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Akarsu Ayazoglu T, Ozensoy A, Geyik FD, Calim M, Duman U, Candan MA. Effects of combined epidural analgesia with total intravenous anesthesia on risky patients underwent major abdominal surgery. Agri 2015;27(4):171‐80. [PUBMED: 26860490] - PubMed
Ali 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ali M, Winter DC, Hanly AM, O'Hagan C, Keaveny J, Broe P. Prospective, randomized, controlled trial of thoracic epidural or patient‐controlled opiate analgesia on perioperative quality of life. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2010;104(3):292‐7. [PUBMED: 20124282] - PubMed
Astakhov 1984 {published data only}
-
- Astakhov AA, Kuvatov GA, Fokin AA, Verbovetskii LP, Kuvatov VA. Choosing the method of anaesthesia in aortofemoral shunting [Vybor metoda anestezii pri aortobedrennom shuntirovanii.]. Vestnik Khirurgii Imeni I. I. Grekova 1984;133(12):73‐5. [PUBMED: 6528452] - PubMed
Baron 1991 {published data only}
-
- Baron JF, Bertrand M, Barre E, Godet G, Mundler O, Coriat P, et al. Combined epidural and general anaesthesia versus general anaesthesia for abdominal aortic surgery. Anesthesiology 1991;75(4):611‐8. [PUBMED: 1928770] - PubMed
Beilin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Beilin B, Hoofien D, Poran R, Gral I, Grinevich G, Butin B, et al. Comparison of two patient‐controlled analgesia techniques on neuropsychological functioning in the immediate postoperative period. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 2008;30(6):674‐82. [PUBMED: 18612876] - PubMed
Bengtson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Bengtson A, Lannsjo W, Heideman M. Complement and anaphylatoxin responses to cross‐clamping of the aorta. Studies during general anaesthesia with or without extradural blockade. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1987;59(9):1093‐7. [PUBMED: 3499158] - PubMed
Bonnet 1989 {published data only}
-
- Bonnet F, Touboul C, Picard AM, Vodinh J, Becquemin JP. Neuroleptanesthesia versus thoracic epidural anaesthesia for abdominal aortic surgery. Annals of Vascular Surgery 1989;3(3):214‐9. [PUBMED: 2570604] - PubMed
Borovskikh 1990 {published data only}
-
- Borovskikh NA, Lebedev LV, Strashkov VI, Vinogradov AT. Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of epidural anesthesia with spontaneous respiration and general anesthesia in aorto‐femoral bifurcation shunt [Sravnitel'naia otsenka effektivnosti epidural'noi anestezii so spontannym dykhaniem i obshchei anestezii pri aortobedrennom bifurkatsionnom shuntirovanii.]. Vestnik Khirurgii Imeni I. I. Grekova 1990;145(7):95‐8. [PUBMED: 2176417] - PubMed
Borovskikh 1991a {published data only}
-
- Borovskikh NA, Andrushchuk IuV, Levshankov KA. Changes in various indicators of homeostasis after operation on the abdominal aorta in relation to the method of anaesthesia [Izmeneniia nekotorykh pokazatelei gomeostaza posle operatsii na briushnoi aorte v zavisimosti ot metoda anestezii]. Vestnik Khirurgii Imeni I. I. Grekova 1991;146(3):92‐5. [PUBMED: 1654658] - PubMed
Borovskikh 1991b {published data only}
-
- Borovskikh NA, Filev LV, Luk'ianov IuV. The effect of the methods of anaesthesiological assistance and blood oxygenation on the oxygen‐transport properties of the blood in reconstructive interventions on the abdominal aorta and vessels of the lower extremities [Vliianie metodov anesteziologicheskogo posobiia i oksigenatsii krovi na kislorodtransportnye svoistva krovi pri rekonstruktivnykh vmeshatel'stvakh na briushnoi aorte i sosudakh nizhnikh konechnostei.]. Grudnaia i Serdechno‐Sosudistaia Khirurgiia 1991;11:27‐30. [PUBMED: 1764306] - PubMed
Breslow 1993 {published data only}
-
- Breslow MJ, Parker SD, Frank SM, Norris EJ, Yates H, Raff H, et al. Determinants of catecholamine and cortisol responses to lower extremity revascularization. The PIRAT Study Group. Anesthesiology 1993;79(6):1202‐9. [PUBMED: 8267195] - PubMed
-
- Christopherson R, Glavan NJ, Norris EJ, Beattie C, Rock P, Frank SM, et al. Control of blood pressure and heart rate in patients randomized to epidural or general anaesthesia for lower extremity vascular surgery. Perioperative Ischemia Randomized Anesthesia Trial (PIRAT) Study Group. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 1996;8(7):578‐8. [PUBMED: 8910181] - PubMed
Brinkmann 1994 {published data only}
-
- Brinkmann A, Seeling W, Wolf CF, Kneitinger E, Junger S, Rockemann M, et al. The effect of thoracic epidural anaesthesia on the pathophysiology of the eventration syndrome [Einfluss der Thorakalen Epiduralanasthesie auf die Pathophysiologie des Eventrationssyndroms]. Der Anaesthesist 1994;43(4):235‐44. [PUBMED: 8179173] - PubMed
Brustia 2003 {published data only}
-
- Brustia P, Renghi A, Gramaglia L, Porta C, Cassatella R, Angelis R, et al. Mininvasive abdominal aortic surgery. Early recovery and reduced hospitalization after multidisciplinary approach. Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery 2003;44(5):629‐35. [PUBMED: 14735052] - PubMed
Bunt 1987 {published data only}
-
- Bunt TJ, Manczuk M, Varley K. Continuous epidural anaesthesia for aortic surgery: thoughts on peer review and safety. Surgery 1987;101(6):706‐14. [PUBMED: 3589965] - PubMed
Diebel 1987 {published data only}
-
- Diebel LN, Lange MP, Schneider F, Mason K, Wilson RF, Jacobs L, et al. Cardiopulmonary complications after major surgery: a role for epidural analgesia?. Surgery 1987;102(4):660‐6. [PUBMED: 3660241] - PubMed
Dodds 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dodds TM, Burns AK, DeRoo DB, Plehn JF, Haney M, Griffin BP, et al. Effects of anaesthetic technique on myocardial wall motion abnormalities during abdominal aortic surgery. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anaesthesia 1997;11(2):129‐36. [PUBMED: 9105980] - PubMed
Donatelli 2006 {published data only}
-
- Donatelli F, Schricker T, Parrella P, Asenjo F, Wykes L, Carli F. Intraoperative infusion of amino acids induces anabolism independent of the type of anaesthesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2006;103(6):1549‐56. [PUBMED: 17122238] - PubMed
Dylczyk‐Sommer 2015 {published data only}
-
- Dylczyk‐Sommer J, Owczuk R, Wujtewicz M, Wojciechowski J. Does epidural anaesthesia reduce the incidence of postoperative oxygen desaturation episodes in patients undergoing open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair?. Anaesthesiology Intensive Therapy 2015;47(4):291‐6. [PUBMED: 26401734] - PubMed
Ederoth 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ederoth P, Flisberg P, Ungerstedt U, Nordstrom CH, Lundberg J. Local metabolic changes in subcutaneous adipose tissue during intravenous and epidural analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2002;46(5):585‐91. [PUBMED: 12027854] - PubMed
Fernandez 1990 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez JA, Casas JI, Villar Landeira JM. Epidural analgesia versus conventional intravenous analgesia after aortic surgery [Analgesia epidural versus analgesia convencional intravenosa, tras cirugia aortica]. Revista Espanola de Anestesiologia y Reanimacion 1990; Vol. 37, issue 5:309‐10. [PUBMED: 2098867] - PubMed
George 1992 {published data only}
-
- George KA, Chisakuta AM, Gamble JA, Browne GA. Thoracic epidural infusion for postoperative pain relief following abdominal aortic surgery: bupivacaine, fentanyl or a mixture of both?. Anaesthesia 1992;47(5):388‐94. [PUBMED: 1599061] - PubMed
Gibbs 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gibbs NM, Crawford GP, Michalopoulos N. The effect of epidural blockade on postoperative hypercoagulability following abdominal aortic bypass surgery. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 1992;20(4):487‐90. [PUBMED: 1463179] - PubMed
Gold 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gold MS, DeCrosta D, Rizzuto C, Ben‐Harari RR, Ramanathan S. The effect of lumbar epidural and general anaesthesia on plasma catecholamines and haemodynamics during abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1994;78(2):225‐30. [PUBMED: 8311273] - PubMed
Goldmann 2008 {published data only}
-
- Goldmann A, Hoehne C, Fritz GA, Unger J, Ahlers O, Nachtigall I, et al. Combined vs. isoflurane/fentanyl anaesthesia for major abdominal surgery: effects on hormones and haemodynamics. Medical Science Monitor 2008;14(9):CR445‐52. [PUBMED: 18758414] - PubMed
Her 1990 {published data only}
-
- Her C, Kizelshteyn G, Walker V, Hayes D, Lees DE. Combined epidural and general anaesthesia for abdominal aortic surgery. Journal of Cardiothoracic Anaesthesia 1990;4(5):552‐7. [PUBMED: 2132133] - PubMed
Houweling 1993 {published data only}
-
- Houweling PL, Ionescu TI, Leguit P, Tweel I, Smalhout B. Comparison of the cardiovascular effects of intravenous, epidural and intrathecal sufentanil analgesia as a supplement to general anaesthesia for abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 1993;10(6):403‐11. [PUBMED: 11767316] - PubMed
Hu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hu Y, Wang Y, Li Y. Effects of different analgesic methods on immune function after lower abdominal surgery. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;10(4):62‐4.
Katz 1992 {published data only}
-
- Katz S, Reiten P, Kohl R. The use of epidural anaesthesia and analgesia in aortic surgery. American Surgeon 1992;58(8):470‐3. [PUBMED: 1642382] - PubMed
Kawasaki 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kawasaki T, Ogata M, Kawasaki C, Okamoto K, Sata T. Effects of epidural anaesthesia on surgical stress‐induced immunosuppression during upper abdominal surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2007;98(2):196‐203. [PUBMED: 17218378] - PubMed
Lombardo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lombardo L, Ruggia O, Crocella L, Masoero G, Foti M, Mambrini S, et al. Epidural plus general anaesthesia vs general anaesthesia alone for elective aortic surgery: effects on gastric electrical activity and serum gastrin secretion. Minerva Anestesiologica 2009;75(3):109‐15. [PUBMED: 19221543 ] - PubMed
Lundberg 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lundberg J, Lundberg D, Norgren L, Ribbe E, Thorne J, Werner O. Intestinal haemodynamics during laparotomy: effects of thoracic epidural anaesthesia and dopamine in humans. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1990;71(1):9‐15. [PUBMED: 2194404] - PubMed
Mason 1990 {published data only}
-
- Mason RA, Newton GB, Cassel W, Maneksha F, Giron F. Combined epidural and general anaesthesia in aortic surgery. Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery 1990;31(4):442‐7. [PUBMED: 2211796] - PubMed
Misquith 2016 {published data only}
Mohapatra 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mohapatra, S, Nayak RS, Jena P, Tripathy SK, Das SR. A study of changes in stress factors during elective upper abdominal surgery using different anaesthetic techniques. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research 2016;39(1):167‐72.
Murakami 2009 {published data only}
-
- Murakami T, Okuda Y, Ishii M, Kobayashi A, Kawamura M. Comparison of intravenous fentanyl analgesia and epidural analgesia for postoperative pain relief. Masui Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2009;58(9):1149‐53. - PubMed
Pan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Pan LF, Wang DX, Li J. Effects of different methods of anaesthesia and analgesia on early postoperative cognitive dysfunction after non‐cardiac surgery in the elderly. Journal of Peking University 2006;38(5):510‐4. - PubMed
Panaretou 2012 {published data only}
-
- Panaretou V, Siafaka I, Theodorou D, Manouras A, Seretis C, Gourgiotis S, et al. Combined general‐epidural anaesthesia with continuous postoperative epidural analgesia preserves sigmoid colon perfusion in elective infrarenal aortic aneurysm repair. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia 2012;6(4):373‐9. [PUBMED: 23493852] - PMC - PubMed
Pecoraro 1990 {published data only}
-
- Pecoraro JP, Dardik H, Mauro A, Wolodiger F, Drascher G, Raccuia S, et al. Epidural anaesthesia as an adjunct to retroperitoneal aortic surgery. American Journal of Surgery 1990;160(2):187‐91. [PUBMED: 2382772] - PubMed
Piper 2000 {published data only}
-
- Miller DR. Retraction note to: Hemodynamics, intramucosal pH and regulators of circulation during perioperative epidural analgesia. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2011;58(9):889‐90. [PUBMED: 2179270] - PubMed
-
- Piper SN, Boldt J, Schmidt CC, Maleck WH, Brosch C, Kumle B. Haemodynamics, intramucosal pH and regulators of circulation during perioperative epidural analgesia. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2000;47(7):631‐7. [PUBMED: 10930202] - PubMed
Renghi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Renghi A, Gramaglia L, Casella F, Moniaci D, Gaboli K, Brustia P. Local versus epidural anaesthesia in fast‐track abdominal aortic surgery. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 2013;27(3):451‐8. [PUBMED: 23273683] - PubMed
Rosseel 1985 {published data only}
-
- Rosseel P, Marichal P, Lauwers LF, Baute L, Hanegreefs G. A haemodynamic study of epidural versus intravenous anaesthesia for aortofemoral bypass surgery. Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica 1985;36(4):345‐63. [PUBMED: 4096193] - PubMed
Saada 1992 {published data only}
-
- Saada M, Catoire P, Bonnet F, Delaunay L, Gormezano G, Macquin‐Mavier I, et al. Effect of thoracic epidural anaesthesia combined with general anaesthesia on segmental wall motion assessed by transoesophageal echocardiography. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1992;75(3):329‐35. [PUBMED: 1510252] - PubMed
Salman 2013 {published data only}
Sayed Moawad 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sayed Moawad H, Mokbel EM. Postoperative analgesia after major abdominal surgery: Fentanyl‐bupivacaine patient controlled epidural analgesia versus fentanyl patient controlled intravenous analgesia. Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia 2014;30:390‐7.
Seeling 1985a {published data only}
-
- Seeling W, Ahnefeld FW, Rosenberg G, Heinrich H, Spilker D. Aortofemoral bifurcation bypass ‐ effect of anaesthesia procedure (NLA, thoracic continuous catheter peridural anaesthesia) on circulation, respiration and metabolism. Hemodynamic changes caused by peridural anaesthesia and anaesthesia induction [Aortofemoraler Bifurkationsbypass ‐ der Einfluss des Anaesthesieverfahrens (NLA, thorakale kontinuierliche Katheterperiduralanaesthesie) auf Kreislauf, Atmung und Stoffwechsel]. Anaesthesist 1985;34(5):217‐28. [PUBMED: 4025792] - PubMed
Seeling 1985b {published data only}
-
- Seeling W, Ahnefeld FW, Hamann H, Heinrich H, Hutschenreiter S, Rosenberg G, et al. Aortofemoral bifurcation bypass ‐ effect of the anesthesia procedure (NLA, thoracic continuous catheter peridural anesthesia) on circulation, respiration and metabolism. Intraoperative circulatory reactions [Aortofemoraler Bifurkationsbypass ‐ Der Einfluss des Anaesthesieverfahrens (NLA, thorakale kontinuierliche Katheterperiduralanaesthesie) auf Kreislauf, Atmung und Stoffwechsel. Intraoperatives Kreislaufverhalten]. Anaesthesist 1985;34(9):417‐28. [PUBMED: 3909840] - PubMed
Seeling 1986 {published data only}
-
- Seeling W, Ahnefeld FW, Grunert A, Heinrich H, Lotz P, Rosenberg G, et al. Aortofemoral bifurcation bypass. Effect of the anaesthesia procedure (NLA, thoracic continuous catheter peridural anesthesia) on circulation, respiration and metabolism. Homeostasis and oxygen transport [Aortofemoraler Bifurkationsbypass. Der Einfluss des Anaesthesie‐verfahrens (NLA, thorakale kontinuierliche Katheterperidural‐anaesthesie) auf Kreislauf, Atmung und Stoffwechsel. Homoostase und Sauerstofftransport]. Anaesthesist 1986;35(2):80‐92. [PUBMED: 3963358] - PubMed
Seeling 1990 {published data only}
-
- Seeling W, Bruckmooser KP, Hufner C, Kneitinger E, Rigg C, Rockemann M. No reduction in postoperative complications by the use of catheterized epidural analgesia following major abdominal surgery [Keine Verminderung postoperativer Komplikationen durch Katheterepiduralanalgesie nach grossen abdominellen Eingriffen]. Anaesthesist 1990;39(1):33‐40. [PUBMED: 2407144] - PubMed
Seeling 1991 {published data only}
-
- Seeling W, Bothner U, Eifert B, Rockemann M, Schreiber M, Schurmann W, et al. Patient‐controlled analgesia versus epidural analgesia using bupivacaine or morphine following major abdominal surgery. No difference in postoperative morbidity [Patientenkontrollierte Analgesie versus Epiduralanalgesie mit Bupivacain oder Morphin nach grossen abdominellen Eingriffen. Kein Unterschied in der postoperativen Morbiditat]. Anaesthesist 1991;40(11):614‐23. [PUBMED: 1755532] - PubMed
Smeets 1993 {published data only}
-
- Smeets HJ, Kievit J, Dulfer FT, Kleef JW, Bonnet F. Endocrine‐metabolic response to abdominal aortic surgery: a randomized trial of general anaesthesia versus general plus epidural anaesthesia. World Journal of Surgery 1993;17(5):601‐7. - PubMed
Tatsuishi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Tatsuishi W, Kohri T, Kodera K, Asano R, Kataoka G, Kubota S, et al. Usefulness of an enhanced recovery after surgery protocol for perioperative management following open repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Surgery Today 2012;42(12):1195‐200. [PUBMED: 22797961] - PubMed
Thierry 1983 {published data only}
-
- Thierry M, Corre A, Haddad C, Becade P. Place of peridural anaesthesia in aorto‐iliac surgery. Preliminary comparative study apropos of 32 patients [Place de l'anesthésie péridurale en chirurgie aorto‐iliaque. Etude préliminaire comparative à propos de 32 patients]. Journal des Maladies Vasculaires 1983;8(4):329‐33. [PUBMED: 6663204] - PubMed
Tilleul 2012 {published data only}
-
- Tilleul P, Aissou M, Bocquet F, Thiriat N, Grelle O, Burke MJ, et al. Cost‐effectiveness analysis comparing epidural, patient‐controlled intravenous morphine, and continuous wound infiltration for postoperative pain management after open abdominal surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2012;108(6):998‐1005. [PUBMED: 22466819] - PubMed
Tuman 1991 {published data only}
-
- Tuman KJ, McCarthy RJ, March RJ, DeLaria GA, Patel RV, Ivankovich AD. Effects of epidural anaesthesia and analgesia on coagulation and outcome after major vascular surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1991;73(6):696‐704. [PUBMED: 1952169] - PubMed
Vabishchevich 1986 {published data only}
-
- Vabishchevich AV, Ginzburg LS, Lemenev VL, Titov AA. Use of epidural anesthesia in middle‐aged and elderly patients for operations in the aortofemoral area [Primenenie epidural'noi anestezii u bol'nykh pozhilogo i starcheskogo vozrasta pri operatsiiakh v aortobedrennoi zone]. Anesteziologiia i Reanimatologiia 1986;5:66‐7. [PUBMED: 3813114] - PubMed
Vaisanen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Vaisanen O, Parviainen I, Ruokonen E, Hippelainen M, Berg E, Hendolin H, et al. Epidural analgesia with bupivacaine does not improve splanchnic tissue perfusion after aortic reconstruction surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1998;81(6):893‐8. [PUBMED: 10211015] - PubMed
Wilhelm 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wilhelm AJ, Dieleman HG. Epidural fentanyl and sufentanil for intra‐ and postoperative analgesia. A randomized, double‐blind comparison. Pharmacy World and Science 1994;16(1):7‐12. [PUBMED: 8156047] - PubMed
Wust 1980 {published data only}
-
- Wust HJ, Spirgatis WD, Sandmann W, Krian A, Richter O. The effects of different anaesthetic technics on lactate under the course of aorto‐femoral bypass operation [Laktatverhalten wahrend aorto‐femoraler Bypassoperationen unter verschiedenen Narkoseverfahren]. Anasthesie, Intensivtherapie, Notfallmedizin 1980;15(2):87‐98. [PUBMED: 6772048] - PubMed
Wust 1982 {published data only}
-
- Wust HJ, Feiereis HW, Sandmann W, Florack G. [lood volume in aorto‐femoral bypass operation. Effects of continuous thoracic epidural‐, halothane‐ or neuroleptanaesthesia [Blutvolumen bei aortofemoralen Bypass‐Operationen. Einfluss der kontinuierlichen thorakalen Epiduralanaesthesie, Halothannarkose und Neuroleptanaesthesie]. Anaesthesist 1982;31(9):449‐55. [PUBMED: 7149218] - PubMed
Yardeni 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yardeni IZ, Shavit Y, Bessler H, Mayburd E, Grinevich G, Beilin B. Comparison of postoperative pain management techniques on endocrine response to surgery: a randomised controlled trial. International Journal of Surgery 2007;5(4):239‐43. [PUBMED: 17660130] - PubMed
Yuceyar 2004 {published data only}
-
- Yuceyar L, Erolcay H, Konukoglu D, Bozkurt AK, Aykac B. Epidural anesthesia may attenuate lipid peroxidation during aorto‐femoral surgery. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2004;51(5):465‐71. [PUBMED: 15128632] - PubMed
Zhang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zhang J, Zhang W, Li B. The effect of epidural anaesthesia with different concentrations of ropivacaine on sevoflurane requirements. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2007;104(4):984‐6. [PUBMED: 17377119] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Owczuk 2016 {published data only}
-
- Owczuk R, Dylczyk‐Sommer A, Wojciechowski J, Paszkiewicz M, Wujtewicz M, Stepnowski P, et al. The influence of epidural blockade on gut permeability in patients undergoing open surgical repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Anaesthesiology Intensive Therapy 2016;48(2):122‐7. [PUBMED: 26965722] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Li 2015 {published data only}
-
- Li YW, Li HJ, Li HJ, Feng Y, Yu Y, Guo XY, et al. Effects of two different anesthesia‐analgesia methods on incidence of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing major thoracic and abdominal surgery: study rationale and protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiology 2015;15:144. [PUBMED: 26459347] - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Block 2003
-
- Block BM, Liu SS, Rowlingston AJ, Cowan JA, Wu CL. Efficacy of postoperative epidural analgesia. JAMA 2003;290(18):2455‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Guay 2006
-
- Guay J. The benefits of adding epidural analgesia to general anaesthesia: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Anesthesia 2006;20(4):335‐40. [PUBMED: 17072704] - PubMed
Guay 2013
-
- Guay J, Ochroch EA. Beta‐blocking agents for surgery: influence on mortality and major outcomes. A meta‐analysis. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 2013;27(5):834‐44. [PUBMED: 23790500] - PubMed
Guay 2014a
Guay 2014b
-
- Guay J, Ochroch EA. Effects of adding statins before surgery on mortality and major morbidity: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 2014;28(2):255‐66. [PUBMED: 24011872] - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction ‐ GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. [PUBMED: 21195583] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011b
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, et al. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence ‐ indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1303‐10. [PUBMED: 21802903] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011c
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines: 6. Rating the quality of evidence ‐ imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283‐93. [PUBMED: 21839614] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011d
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 9. Rating up the quality of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1311‐6. [PUBMED: 21802902] - PubMed
Hebl 2006
-
- Hebl JR, Kopp SL, Schroeder DR, Horlocker TT. Neurologic complications after neuraxial anaesthesia or analgesia in patients with preexisting peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy or diabetic polyneuropathy. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2006;103(5):1294‐9. [PUBMED: 17056972] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, 2011.
Horlocker 2010
-
- Horlocker TT, Wedel DJ, Rowlingson JC, Enneking FK, Kopp SL, Benzon HT, et al. Regional anaesthesia in the patient receiving antithrombotic or thrombolytic therapy: American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Evidence‐Based Guidelines (Third Edition). Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine 2010;35(1):64‐101. [PUBMED: 20052816] - PubMed
Jorgensen 2000
-
- Jorgensen H, Wetterslev J, Moiniche S, Dahl JB. Epidural local anaesthetics versus opioid‐based analgesic regimens on postoperative gastrointestinal paralysis, PONV and pain after abdominal surgery. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2000, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001893] - DOI - PubMed
Pace 2011
-
- Pace NL. Research methods for meta‐analyses. Best practice & research. Clinical Anaesthesiology 2011;25(4):523‐33. [PUBMED: 22099918] - PubMed
Paravastu 2014
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Robertson 2014
Rucker 2011
-
- Rucker G, Schwarzer G, Carpenter JR, Binder H, Schumacher M. Treatment‐effect estimates adjusted for small‐study effects via a limit meta‐analysis. Biostatistics (Oxford, England) 2011;12(1):122‐42. [PUBMED: 20656692] - PubMed
Sampson 2014
-
- Sampson UK, Norman PE, Fowkes FG, Aboyans V, Song Y, Harrell FE Jr, et al. Estimation of global and regional incidence and prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms 1990 to 2010. Global Heart 2014; Vol. 9, issue 1:159‐70. [PUBMED: 25432125] - PubMed
Svensjo 2014
-
- Svensjo S, Bjorck M, Wanhainen A. Update on screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: a topical review. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery 2014; Vol. 48, issue 6:659‐67. [PUBMED: 25443524] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Nishimori 2004
Nishimori 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

