The agr Inhibitors Solonamide B and Analogues Alter Immune Responses to Staphylococccus aureus but Do Not Exhibit Adverse Effects on Immune Cell Functions
- PMID: 26731096
- PMCID: PMC4701192
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145618
The agr Inhibitors Solonamide B and Analogues Alter Immune Responses to Staphylococccus aureus but Do Not Exhibit Adverse Effects on Immune Cell Functions
Abstract
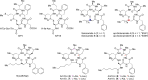
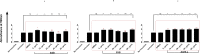
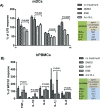
Staphylococcus aureus infections are becoming increasingly difficult to treat due to antibiotic resistance with the community-associated methicillin-resistant S. aureus (CA-MRSA) strains such as USA300 being of particular concern. The inhibition of bacterial virulence has been proposed as an alternative approach to treat multi-drug resistant pathogens. One interesting anti-virulence target is the agr quorum-sensing system, which regulates virulence of CA-MRSA in response to agr-encoded autoinducing peptides. Agr regulation confines exotoxin production to the stationary growth phase with concomitant repression of surface-expressed adhesins. Solonamide B, a non-ribosomal depsipeptide of marine bacterial origin, was recently identified as a putative anti-virulence compound that markedly reduced expression of α-hemolysin and phenol-soluble modulins. To further strengthen solonamide anti-virulence candidacy, we report the chemical synthesis of solonamide analogues, investigation of structure-function relationships, and assessment of their potential to modulate immune cell functions. We found that structural differences between solonamide analogues confer significant differences in interference with agr, while immune cell activity and integrity is generally not affected. Furthermore, treatment of S. aureus with selected solonamides was found to only marginally influence the interaction with fibronectin and biofilm formation, thus addressing the concern that application of compounds inducing an agr-negative state may have adverse interactions with host factors in favor of host colonization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Plata K, Rosato AE, Wegrzyn G. Staphylococcus aureus as an infectious agent: overview of biochemistry and molecular genetics of its pathogenicity. Acta Biochim Pol 2009. November 12;56(4):597–612. - PubMed
-
- Bien J, Sokolova O, Bozko P. Characterization of Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus aureus: Novel Function of Known Virulence Factors That Are Implicated in Activation of Airway Epithelial Proinflammatory Response. Journal of Pathogens 2011. September 14; (2011: 601905). 10.4061/2011/601905 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Queck SY, Jameson-Lee M, Villaruz AE, Bach TH, Khan BA, Sturdevant DE, et al. RNAIII-independent target gene control by the agr quorum-sensing system: insight into the evolution of virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Cell 2008. October 10;32(1):150–8. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

