The properties of spontaneous mutations in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 26732503
- PMCID: PMC4702332
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-2244-3
The properties of spontaneous mutations in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
Background: Natural genetic variation ultimately arises from the process of mutation. Knowledge of how the raw material for evolution is produced is necessary for a full understanding of several fundamental evolutionary concepts. We performed a mutation accumulation experiment with wild-type and mismatch-repair deficient, mutator lines of the pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and used whole-genome sequencing to reveal the genome-wide rate, spectrum, distribution, leading/lagging bias, and context-dependency of spontaneous mutations.
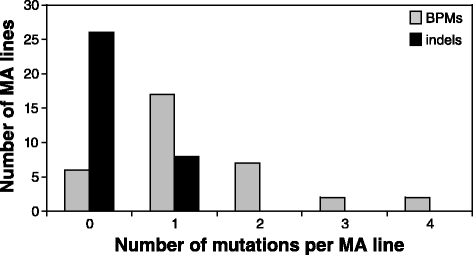
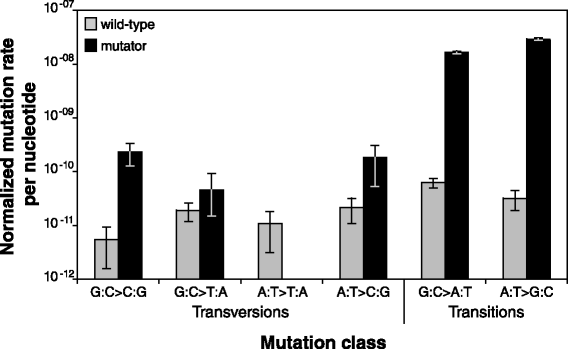
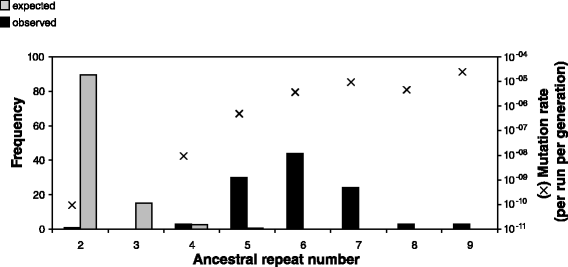
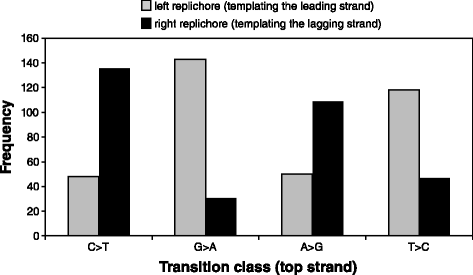
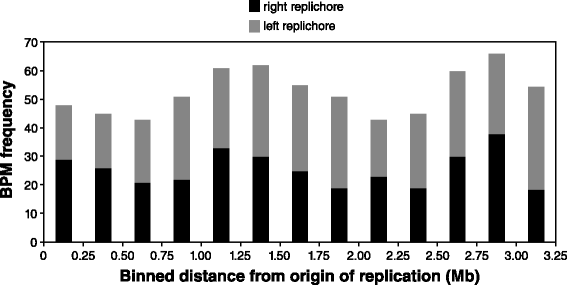
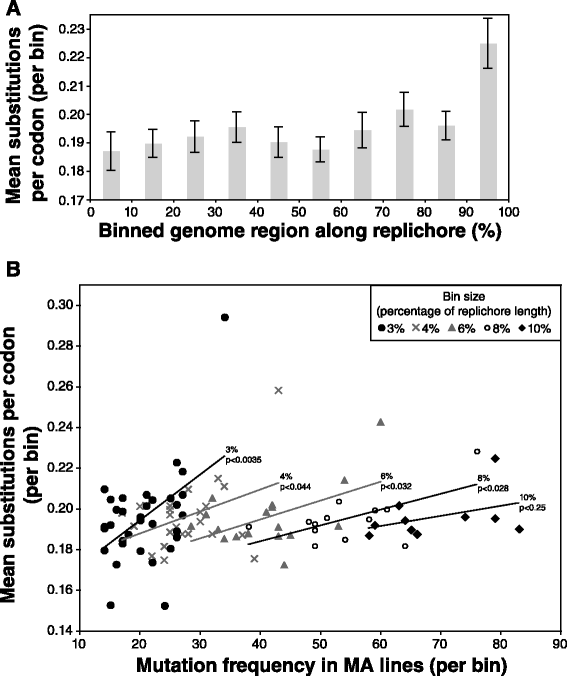
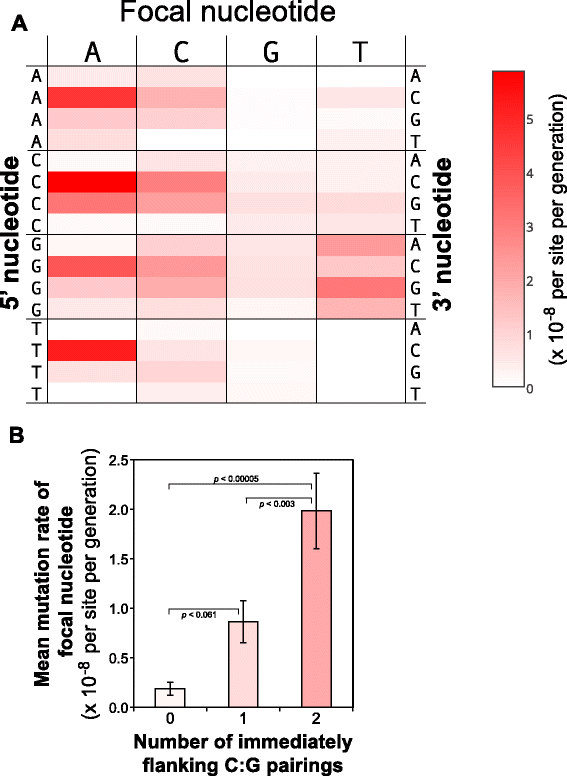
Results: Wild-type base-pair mutation and indel rates were ~10(-10) and ~10(-11) per nucleotide per generation, respectively, and deficiencies in the mismatch-repair system caused rates to increase by over two orders of magnitude. A universal bias towards AT was observed in wild-type lines, but was reversed in mutator lines to a bias towards GC. Biases for which types of mutations occurred during replication of the leading versus lagging strand were detected reciprocally in both replichores. The distribution of mutations along the chromosome was non-random, with peaks near the terminus of replication and at positions intermediate to the replication origin and terminus. A similar distribution bias was observed along the chromosome in natural populations of P. aeruginosa. Site-specific mutation rates were higher when the focal nucleotide was immediately flanked by C:G pairings.
Conclusions: Whole-genome sequencing of mutation accumulation lines allowed the comprehensive identification of mutations and revealed what factors of molecular and genomic architecture affect the mutational process. Our study provides a more complete view of how several mechanisms of mutation, mutation repair, and bias act simultaneously to produce the raw material for evolution.
Figures
References
-
- Kassen R. Experimental Evolution and the Nature of Biodiversity. Greenwood Village (CO): Roberts and Company Publishers; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

