Genetically engineering self-organization of human pluripotent stem cells into a liver bud-like tissue using Gata6
- PMID: 26732624
- PMCID: PMC4729822
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10243
Genetically engineering self-organization of human pluripotent stem cells into a liver bud-like tissue using Gata6
Abstract
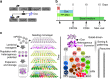
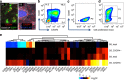
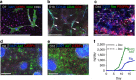
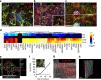
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) have potential for personalized and regenerative medicine. While most of the methods using these cells have focused on deriving homogenous populations of specialized cells, there has been modest success in producing hiPSC-derived organotypic tissues or organoids. Here we present a novel approach for generating and then co-differentiating hiPSC-derived progenitors. With a genetically engineered pulse of GATA-binding protein 6 (GATA6) expression, we initiate rapid emergence of all three germ layers as a complex function of GATA6 expression levels and tissue context. Within 2 weeks we obtain a complex tissue that recapitulates early developmental processes and exhibits a liver bud-like phenotype, including haematopoietic and stromal cells as well as a neuronal niche. Collectively, our approach demonstrates derivation of complex tissues from hiPSCs using a single autologous hiPSCs as source and generates a range of stromal cells that co-develop with parenchymal cells to form tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
P.G., M.R.E. and R.W. filed a patent application (‘Engineering a heterogeneous tissue form pluripotent stem cells', PCT/US2014/031050).
Figures


References
-
- Blanpain C. et al.. Stem cells assessed. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 471–476 (2012) . - PubMed
-
- Eiraku M. et al.. Self-organizing optic-cup morphogenesis in three-dimensional culture. Nature 472, 51–56 (2011) . - PubMed
-
- Takebe T. et al.. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature 499, 481–484 (2013) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

