Basal cell adenoma in the deep portion of the parotid gland: a case report
- PMID: 26733071
- PMCID: PMC4699939
- DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.6.352
Basal cell adenoma in the deep portion of the parotid gland: a case report
Abstract
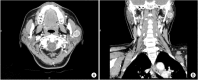
Basal cell adenoma (BCA) is a rare, benign neoplasm that most frequently arises in the parotid gland. We treated a 54-year-old female patient with BCA that had developed in the deep portion of the left parotid gland. The patient presented with gradual facial swelling with no other symptoms. We performed a total parotidectomy to excise the mass, but we preserved the facial nerve. Histopathology revealed a well-encapsulated mass. The tumor was composed of islands of comparatively uniform, small, dark, basaloid epithelial cells in the stroma. Histologic and immunohistochemical studies concluded that the BCA tumors were mostly trabecular. Postoperatively, there was no facial nerve weakness, and the tumor did not recur during the 24-month follow-up period.
Keywords: Basal cell adenoma; Facial nerve preservation; Parotid gland.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Vicandi B, Jiménez-Heffernan JA, López-Ferrer P, González-Peramato P, Patrón M, Viguer JM. Fine needle aspiration cytology of basal cell adenoma of the salivary gland: a cytohistological correlation study of 35 cases. Cytopathology. 2012;23:315–319. - PubMed
-
- González-García R, Nam-Cha SH, Muñoz-Guerra MF, Gamallo-Amat C. Basal cell adenoma of the parotid gland: case report and review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006;11:E206–E209. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

