Increased IGFBP-1 phosphorylation in response to leucine deprivation is mediated by CK2 and PKC
- PMID: 26733150
- PMCID: PMC4811673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.12.006
Increased IGFBP-1 phosphorylation in response to leucine deprivation is mediated by CK2 and PKC
Abstract
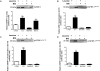
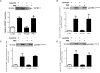
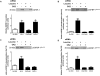
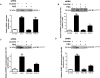
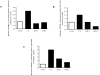
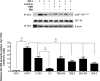
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), secreted by fetal liver, is a key regulator of IGF-I bioavailability and fetal growth. IGFBP-1 phosphorylation decreases IGF-I bioavailability and diminishes its growth-promoting effects. Growth-restricted fetuses have decreased levels of circulating essential amino acids. We recently showed that IGFBP-1 hyperphosphorylation (pSer101/119/169) in response to leucine deprivation is regulated via activation of the amino acid response (AAR) in HepG2 cells. Here we investigated nutrient-sensitive protein kinases CK2/PKC/PKA in mediating IGFBP-1 phosphorylation in leucine deprivation. We demonstrated that leucine deprivation stimulated CK2 activity (enzymatic assay) and induced IGFBP-1 phosphorylation (immunoblotting/MRM-MS). Inhibition (pharmacological/siRNA) of CK2/PKC, but not PKA, prevented IGFBP-1 hyperphosphorylation in leucine deprivation. PKC inhibition also prevented leucine deprivation-stimulated CK2 activity. Functionally, leucine deprivation decreased IGF-I-induced-IGF-1R autophosphorylation when CK2/PKC were not inhibited. Our data strongly support that PKC promotes leucine deprivation-induced IGFBP-1 hyperphosphorylation via CK2 activation, mechanistically linking decreased amino acid availability and reduced fetal growth.
Keywords: Amino acid restriction; Fetal growth; HepG2 cells; Insulin-like growth Factor-1 receptor; Insulin-like growth factor binding protein; Mass spectrometry; Phosphorylation sites; Protein kinases.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


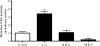
References
-
- Abu Shehab M, Iosef C, Wildgruber R, Sardana G, Gupta MB. Phosphorylation of IGFBP-1 at discrete sites elicits variable effects on IGF-I receptor autophosphorylation. Endocrinology. 2013;154:1130–1143. - PubMed
-
- Abu Shehab M, Khosravi J, Han VK, Shilton BH, Gupta MB. Site-specific IGFBP-1 hyper-phosphorylation in fetal growth restriction: clinical and functional relevance. J. Proteome Res. 2010;9:1873–1881. - PubMed
-
- Ankrapp DP, Jones JI, Clemmons DR. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 kinases from human hepatoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 1996;60:387–399. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

