The plastidial retrograde signal methyl erythritol cyclopyrophosphate is a regulator of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid crosstalk
- PMID: 26733689
- PMCID: PMC4762391
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erv550
The plastidial retrograde signal methyl erythritol cyclopyrophosphate is a regulator of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid crosstalk
Abstract
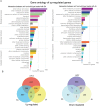
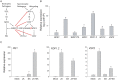
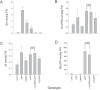
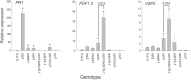
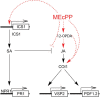
The exquisite harmony between hormones and their corresponding signaling pathways is central to prioritizing plant responses to simultaneous and/or successive environmental trepidations. The crosstalk between jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) is an established effective mechanism that optimizes and tailors plant adaptive responses. However, the underlying regulatory modules of this crosstalk are largely unknown. Global transcriptomic analyses of mutant plants (ceh1) with elevated levels of the stress-induced plastidial retrograde signaling metabolite 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol cyclopyrophosphate (MEcPP) revealed robustly induced JA marker genes, expected to be suppressed by the presence of constitutively high SA levels in the mutant background. Analyses of a range of genotypes with varying SA and MEcPP levels established the selective role of MEcPP-mediated signal(s) in induction of JA-responsive genes in the presence of elevated SA. Metabolic profiling revealed the presence of high levels of the JA precursor 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (OPDA), but near wild type levels of JA in the ceh1 mutant plants. Analyses of coronatine-insensitive 1 (coi1)/ceh1 double mutant plants confirmed that the MEcPP-mediated induction is JA receptor COI1 dependent, potentially through elevated OPDA. These findings identify MEcPP as a previously unrecognized central regulatory module that induces JA-responsive genes in the presence of high SA, thereby staging a multifaceted plant response within the environmental context.
Keywords: Coronatine-insensitive1 (COI1); MEcPP (2-C-methyl-d-erythritol cyclopyrophosphate); hormonal interplay; jasmonic acid (JA); plastidial retrograde signaling metabolite; salicylic acid (SA); stress responses..
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The plastidial metabolite 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate modulates defence responses against aphids.Plant Cell Environ. 2019 Jul;42(7):2309-2323. doi: 10.1111/pce.13538. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Plant Cell Environ. 2019. PMID: 30786032 Free PMC article.
-
Plastidial fatty acid signaling modulates salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-mediated defense pathways in the Arabidopsis ssi2 mutant.Plant Cell. 2003 Dec;15(12):2952-65. doi: 10.1105/tpc.017301. Epub 2003 Nov 13. Plant Cell. 2003. PMID: 14615603 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated omics analyses of retrograde signaling mutant delineate interrelated stress-response strata.Plant J. 2017 Jul;91(1):70-84. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13547. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28370892 Free PMC article.
-
Jasmonate signaling in plant stress responses and development - active and inactive compounds.N Biotechnol. 2016 Sep 25;33(5 Pt B):604-613. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 12. N Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26581489 Review.
-
Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid crosstalk in plant immunity.Essays Biochem. 2022 Sep 30;66(5):647-656. doi: 10.1042/EBC20210090. Essays Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35698792 Review.
Cited by
-
Chloroplast in Plant-Virus Interaction.Front Microbiol. 2016 Oct 4;7:1565. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01565. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27757106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methyl Jasmonate Activates the 2C Methyl-D-erithrytol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate Synthase Gene and Stimulates Tanshinone Accumulation in Salvia miltiorrhiza Solid Callus Cultures.Molecules. 2022 Mar 8;27(6):1772. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061772. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335134 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplast-associated molecular patterns as concept for fine-tuned operational retrograde signalling.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Jun 22;375(1801):20190443. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0443. Epub 2020 May 4. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32362264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDR, the last enzyme in the MEP pathway, differently regulates isoprenoid biosynthesis in two woody plants.Plant Physiol. 2023 May 31;192(2):767-788. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad110. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36848194 Free PMC article.
-
Fluctuating Light Interacts with Time of Day and Leaf Development Stage to Reprogram Gene Expression.Plant Physiol. 2019 Apr;179(4):1632-1657. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01443. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30718349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjornson M, Benn G, Song X, Comai L, Franz AK, Dandekar AM, Drakakaki G, Dehesh K. 2014. Distinct roles for mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and CALMODULIN-BINDING TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVATOR3 in regulating the peak time and amplitude of the plant general stress response. Plant Physiology 166, 988–996. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doherty HM, Selvendran RR, Bowles DJ. 1988. The wound response of tomato plants can be inhibited by aspirin and related hydroxy-benzoic acids. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 33, 377–384.
-
- Fu ZQ, Dong X. 2013. Systemic acquired resistance: turning local infection into global defense. Annual Review of Plant Biology 64, 839–863. - PubMed
-
- Garcion C, Métraux J-P. 2007. Salicylic Acid. Annual Plant Reviews 24, 229–255.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

