Association Between Alzheimer's Disease and Glaucoma: A Study Based on Heidelberg Retinal Tomography and Frequency Doubling Technology Perimetry
- PMID: 26733792
- PMCID: PMC4683203
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00479
Association Between Alzheimer's Disease and Glaucoma: A Study Based on Heidelberg Retinal Tomography and Frequency Doubling Technology Perimetry
Abstract
Aim: To assess the frequency of glaucoma-like alterations in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients using Heidelberg Retinal Tomograph III (HRT-3) and Frequency Doubling Technology (FDT) perimetry.
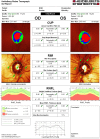
Methods: The study included 51 eyes of 51 AD subjects and 67 eyes of 67 age- and sex-matched controls. Subjects underwent an ophthalmological examination including measurements of intraocular pressure (IOP), Matrix FDT visual field testing, optic nerve head morphology and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (RNFLt) assessment by slit-lamp biomicroscopy and HRT-3.
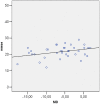
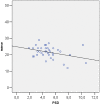
Results: The frequency of alterations was significantly higher in the AD group (27.5 vs. 7.5%; p = 0.003; OR = 4.69). AD patients showed lower IOP (p = 0.000) despite not significantly different values of central corneal thickness (CCT) between the groups (p = 0.336). Of all the stereometric parameters measured by HRT-3, RNFLt was significantly lower in AD patients (p = 0.013). This group also had significantly worse results in terms of Moorfields Regression Analysis (p = 0.027). Matrix showed significantly worse Mean Deviation (MD) (p = 0.000) and Pattern Standard Deviation (PSD) (p = 0.000) values and more altered Glaucoma Hemifield Test (p = 0.006) in AD patients. Pearson's R correlation test showed that Mini Mental State Examination is directly correlated with MD (R = 0.349; p = 0.034) and inversely correlated with PSD (R = -0.357; p = 0.030).
Conclusion: Patients with AD have a higher frequency of glaucoma-like alterations, as detected by the use of HRT-3. These alterations were not associated with elevated IOP or abnormal CCT values.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; CCT; FDT; HRT-3; RNFL; glaucoma; optic nerve head.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between frequency doubling technology and heidelberg retina tomograph.J Glaucoma. 2005 Oct;14(5):368-74. doi: 10.1097/01.ijg.0000176937.93143.bf. J Glaucoma. 2005. PMID: 16148585
-
Relationship between Humphrey 30-2 SITA Standard Test, Matrix 30-2 threshold test, and Heidelberg retina tomograph in ocular hypertensive and glaucoma patients.J Glaucoma. 2008 Apr-May;17(3):203-10. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31815a3493. J Glaucoma. 2008. PMID: 18414106
-
Humphrey matrix frequency doubling technology perimetry and optical coherence tomography measurement of the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in both normal and ocular hypertensive subjects.J Glaucoma. 2006 Aug;15(4):328-35. doi: 10.1097/01.ijg.0000212230.65545.d3. J Glaucoma. 2006. PMID: 16865011
-
Correlation of frequency-doubling perimetry with retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic disc size in ocular hypertensives and glaucoma suspects.J Glaucoma. 2011 Aug;20(6):366-70. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e3181eda96e. J Glaucoma. 2011. PMID: 20717056
-
[Diagnostic approaches for early detection of glaucoma progression].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2006 Mar;223(3):194-216. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-858734. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2006. PMID: 16552653 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Macular ganglion cells alteration in a patient with left homonymous hemianopia subsequent to surgical excision of an arteriovenous malformation.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2018 Aug 1;12:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2018.07.009. eCollection 2018 Dec. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30105312 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoxetine Protects Retinal Ischemic Damage in Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 29;15(5):1370. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051370. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242611 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 30;9(10):3172. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103172. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33007927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thirty Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease Unified by a Common Neuroimmune-Neuroinflammation Mechanism.Brain Sci. 2023 Dec 31;14(1):41. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14010041. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38248256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Sex on Neuroretinal Degeneration: Six-Month Follow-Up in Rats With Chronic Glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Oct 4;62(13):9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.13.9. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34643665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2004). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DMS IV) 4th Edn. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources