Naïve T Cell Homeostasis Regulated by Stress Responses and TCR Signaling
- PMID: 26734005
- PMCID: PMC4681834
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00638
Naïve T Cell Homeostasis Regulated by Stress Responses and TCR Signaling
Abstract
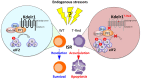
The survival of naïve T cells is believed to require signals from TCR-pMHC interactions and cytokines such as IL-7. In contrast, signals that negatively impact naïve T cell survival are less understood. We conducted a forward genetic screening of mice and found a mutant mouse line with reduced number of naïve T cells (T-Red mice). T-Red mice have a point mutation in the Kdelr1 gene, and their naïve T cells show enhanced integrated stress response (ISR), which eventually induces their apoptosis. Therefore, naïve T cells require a KDEL receptor-mediated mechanism that efficiently relieves cellular stress for their survival in vivo. Interestingly, naïve T cells expressing TCR with higher affinity/avidity to self-antigens survive in T-Red mice, suggesting the possible link between TCR-mediated survival and ISR-induced apoptosis. In this article, we discuss the regulation of naïve T cell homeostasis, keeping special attention on the ISR and TCR signal.
Keywords: T cell homeostasis; TCR signaling; mutagenesis; naive T cells; stress response.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

