HER Specific TKIs Exert Their Antineoplastic Effects on Breast Cancer Cell Lines through the Involvement of STAT5 and JNK
- PMID: 26735495
- PMCID: PMC4703392
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146311
HER Specific TKIs Exert Their Antineoplastic Effects on Breast Cancer Cell Lines through the Involvement of STAT5 and JNK
Abstract
Background: HER-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have demonstrated pro-apoptotic and antiproliferative effects in vitro and in vivo. The exact pathways through which TKIs exert their antineoplastic effects are, however, still not completely understood.
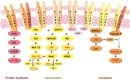
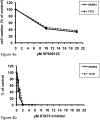
Methods: Using Milliplex assays, we have investigated the effects of the three panHER-TKIs lapatinib, canertinib and afatinib on signal transduction cascade activation in SKBR3, T47D and Jurkat neoplastic cell lines. The growth-inhibitory effect of blockade of HER and of JNK and STAT5 signaling was measured by proliferation- and apoptosis-assays using formazan dye labeling of viable cells, Western blotting for cleaved PARP-1 and immunolabeling for active caspase 3, respectively.
Results: All three HER-TKIs clearly inhibited proliferation and increased apoptosis in HER2 overexpressing SKBR3 cells, while their effect was less pronounced on HER2 moderately expressing T47D cells where they exerted only a weak antiproliferative and essentially no pro-apoptotic effect. Remarkably, phosphorylation/activation of JNK and STAT5A/B were inhibited by HER-TKIs only in the sensitive, but not in the resistant cells. In contrast, phosphorylation/activation of ERK/MAPK, STAT3, CREB, p70 S6 kinase, IkBa, and p38 were equally affected by HER-TKIs in both cell lines. Moreover, we demonstrated that direct pharmacological blockade of JNK and STAT5 abrogates cell growth in both HER-TKI-sensitive as well as -resistant breast cancer cells, respectively.
Conclusion: We have shown that HER-TKIs exert a HER2 expression-dependent anti-cancer effect in breast cancer cell lines. This involves blockade of JNK and STAT5A/B signaling, which have been found to be required for in vitro growth of these cell lines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
HER-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors enhance response to trastuzumab and pertuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2019 Jun;37(3):441-451. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0649-y. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Invest New Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30062574
-
PTK6 inhibition promotes apoptosis of Lapatinib-resistant Her2(+) breast cancer cells by inducing Bim.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 19;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0594-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26084280 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the putative cancer stem cell markers and growth factor receptor expression on the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to treatment with various forms of small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors and cytotoxic drugs.Int J Oncol. 2016 Nov;49(5):1825-1838. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3678. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27599579 Free PMC article.
-
An update of the mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer: Gefitinib (Iressa) -induced changes in the expression and nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of HER-ligands (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2007 Jul;20(1):3-10. Int J Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17549382 Review.
-
The role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of HER2+ metastatic breast cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Sep;154:175-189. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.06.026. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34280871 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Omic Data Interpretation to Repurpose Subtype Specific Drug Candidates for Breast Cancer.Front Genet. 2019 May 7;10:420. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00420. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31134131 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 22;11(10):1618. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101618. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31652660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Drug Screening Reveals Minocycline Hydrochloride as a Therapeutic Option to Prevent Breast Cancer Cells Extravasation across the Blood-Brain Barrier.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 16;10(8):1988. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081988. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009536 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lapatinib on cell proliferation and apoptosis in NB4 cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):235-242. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7342. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29387217 Free PMC article.
-
SCAMP3 Regulates EGFR and Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through the Modulation of AKT, ERK, and STAT3 Signaling Pathways.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 5;14(11):2807. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112807. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendelsohn J. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;20: 1–13. - PubMed
-
- Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7: 505–516. - PubMed
-
- Rusnak DW, Lackey K, Affleck K, Wood ER, Alligood KJ, Rhodes N, et al. The effects of the novel, reversible epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor GW2016, on the growth of human normal and tumor-derived cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2001;1: 85–94. - PubMed
-
- Konecny GE, Pegram MG, Venkatesan N, Finn R, Yang G, Rahmeh M, et al. Activity of the dual kinase inhibitor lapatinib (GW572016) on Her2 overexpressing and trastuzumab- treated breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66: 1630–1639. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

