Recurrent Acute Liver Failure Because of Acute Hepatitis Induced by Organic Solvents: A Case Report
- PMID: 26735550
- PMCID: PMC4706270
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002445
Recurrent Acute Liver Failure Because of Acute Hepatitis Induced by Organic Solvents: A Case Report
Abstract
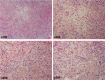
The authors present a case of recurrent acute liver failure because of occupational exposure to organic solvents. A 35-year-old man with a 3-week history of worsening jaundice and flu-like symptoms was admitted to our hospital. Viral hepatitis serology and autoimmune factors were negative. The authors considered liver transplantation, but the patient's liver function spontaneously recovered. Liver biopsy revealed massive infiltration of neutrophils, but the cause of the acute hepatitis was not identified. Four months after discharge, the patient's liver function worsened again. The authors considered the possibility of antinuclear antibody-negative autoimmune hepatitis and initiated steroid treatment, which was effective. Four months after discharge, the patient was admitted for repeated liver injury. The authors started him on steroid pulse therapy, but this time it was not effective. Just before the first admission, he had started his own construction company where he was highly exposed to organic solvents, and thus the authors considered organic solvent-induced hepatitis. Although urine test results for organic solvents were negative, a second liver biopsy revealed severe infiltration of neutrophils, compatible with toxic hepatitis. Again, his liver function spontaneously improved. Based on the pathology and detailed clinical course, including the patient's high exposure to organic solvents since just before the first admission, and the spontaneous recovery of his liver damage in the absence of the exposure, he was diagnosed with toxic hepatitis. The authors strongly advised him to avoid organic solvents. Since then, he has been in good health without recurrence. This is the first report of recurrent acute liver failure because of exposure to organic solvents, which was eventually diagnosed through a meticulous medical history and successfully recovered by avoiding the causative agents. In acute liver failure with an undetermined etiology, clinicians should rule out organic solvent-induced hepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Lee WM. Etiologies of acute liver failure. Semin Liver Dis 2008; 28:142–152. - PubMed
-
- Cash WJ, McConville P, McDermott E. Current concepts in the assessment and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. QJM 2010; 103:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Urata K, Kawasaki S, Matsunami H, et al. Calculation of child and adult standard liver volume for liver transplantation. Hepatology 1995; 21:1317–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

