Interferon Alpha Signalling and Its Relevance for the Upregulatory Effect of Transporter Proteins Associated with Antigen Processing (TAP) in Patients with Malignant Melanoma
- PMID: 26735690
- PMCID: PMC4703378
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146325
Interferon Alpha Signalling and Its Relevance for the Upregulatory Effect of Transporter Proteins Associated with Antigen Processing (TAP) in Patients with Malignant Melanoma
Abstract
Introduction: Interferon alpha (IFNα) is routinely used in the clinical practice for adjuvant systemic melanoma therapy. Understanding the molecular mechanism of IFNα effects and prediction of response in the IFNα therapy regime allows initiation and continuation of IFNα treatment for responder and exclusion of non-responder to avoid therapy inefficacy and side-effects. The transporter protein associated with antigen processing-1 (TAP1) is part of the MHC class I peptide-loading complex, and important for antigen presentation in tumor and antigen presenting cells. In the context of personalized medicine, we address this potential biomarker TAP1 as a target of IFNα signalling.
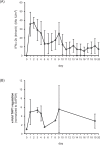
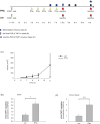
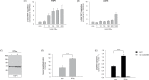
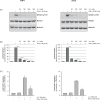
Results: We could show that IFNα upregulates TAP1 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients with malignant melanoma receiving adjuvant high-dose immunotherapy. IFNα also induced expression of TAP1 in mouse blood and tumor tissue and suppressed the formation of melanoma metastasis in an in vivo B16 tumor model. Besides its expression, TAP binding affinity and transport activity is induced by IFNα in human monocytic THP1 cells. Furthermore, our data revealed that IFNα clearly activates phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3 in THP1 and A375 melanoma cells. Inhibition of Janus kinases abrogates the IFNα-induced TAP1 expression. These results suggest that the JAK/STAT pathway is a crucial mediator for TAP1 expression elicited by IFNα treatment.
Conclusion: We suppose that silencing of TAP1 expression provides tumor cells with a mechanism to escape cytotoxic T-lymphocyte recognition. The observed benefit of IFNα treatment could be mediated by the shown dual effect of TAP1 upregulation in antigen presenting cells on the one hand, and of TAP1 upregulation in 'silent' metastatic melanoma cells on the other hand. In conclusion, this work contributes to a better understanding of the mode of action of IFNα which is essential to identify markers to predict, assess and monitor therapeutic response of IFNα treatment in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC Jr. Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(1):51–65. - PubMed
-
- Baron JM, Heise R, Merk HF, Abuzahra F. Current and future directions in the treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003;3(6):393–8. - PubMed
-
- Eggermont AM, Suciu S, MacKie R, Ruka W, Testori A, Kruit W, et al. Post-surgery adjuvant therapy with intermediate doses of interferon alfa 2b versus observation in patients with stage IIb/III melanoma (EORTC 18952): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366(9492):1189–96. - PubMed
-
- Eggermont AM, Suciu S, Santinami M, Testori A, Kruit WH, Marsden J, et al. Adjuvant therapy with pegylated interferon alfa-2b versus observation alone in resected stage III melanoma: final results of EORTC 18991, a randomised phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9633):117–26. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61033-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sondak VK, Richards J, Flaherty LE, Ernstoff MS, et al. High- and low-dose interferon alfa-2b in high-risk melanoma: first analysis of intergroup trial E1690/S9111/C9190. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(12):2444–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

