Road Traffic Injury Prevention Initiatives: A Systematic Review and Metasummary of Effectiveness in Low and Middle Income Countries
- PMID: 26735918
- PMCID: PMC4703343
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144971
Road Traffic Injury Prevention Initiatives: A Systematic Review and Metasummary of Effectiveness in Low and Middle Income Countries
Erratum in
-
Correction: Road Traffic Injury Prevention Initiatives: A Systematic Review and Metasummary of Effectiveness in Low and Middle Income Countries.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0150150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150150. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26894996 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Road traffic injuries (RTIs) are a growing but neglected global health crisis, requiring effective prevention to promote sustainable safety. Low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) share a disproportionately high burden with 90% of the world's road traffic deaths, and where RTIs are escalating due to rapid urbanization and motorization. Although several studies have assessed the effectiveness of a specific intervention, no systematic reviews have been conducted summarizing the effectiveness of RTI prevention initiatives specifically performed in LMIC settings; this study will help fill this gap.
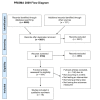
Methods: In accordance with PRISMA guidelines we searched the electronic databases MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus, Web of Science, TRID, Lilacs, Scielo and Global Health. Articles were eligible if they considered RTI prevention in LMICs by evaluating a prevention-related intervention with outcome measures of crash, RTI, or death. In addition, a reference and citation analysis was conducted as well as a data quality assessment. A qualitative metasummary approach was used for data analysis and effect sizes were calculated to quantify the magnitude of emerging themes.
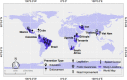
Results: Of the 8560 articles from the literature search, 18 articles from 11 LMICs fit the eligibility and inclusion criteria. Of these studies, four were from Sub-Saharan Africa, ten from Latin America and the Caribbean, one from the Middle East, and three from Asia. Half of the studies focused specifically on legislation, while the others focused on speed control measures, educational interventions, enforcement, road improvement, community programs, or a multifaceted intervention.
Conclusion: Legislation was the most common intervention evaluated with the best outcomes when combined with strong enforcement initiatives or as part of a multifaceted approach. Because speed control is crucial to crash and injury prevention, road improvement interventions in LMIC settings should carefully consider how the impact of improvements will affect speed and traffic flow. Further road traffic injury prevention interventions should be performed in LMICs with patient-centered outcomes in order to guide injury prevention in these complex settings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Organization WH. WHO global status report on road safety 2013: supporting a decade of action 2013, World Health Organization.
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. The global burden of disease and injury series, volume 1: a comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from diseases, injuries, and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020. Cambridge. MA, 1996.
-
- Organization WH. World Report on Road Traffic Injury Prevention; 2004 2008, World Health Organization.: Geneva.
-
- Peden M, et al. World report on road traffic injury prevention World Health Organization. in Hyder AA, Jarawan E, Mathers C. 2004. Citeseer.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous