A Novel Platform for the Potentiation of Therapeutic Antibodies Based on Antigen-Dependent Formation of IgG Hexamers at the Cell Surface
- PMID: 26736041
- PMCID: PMC4703389
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002344
A Novel Platform for the Potentiation of Therapeutic Antibodies Based on Antigen-Dependent Formation of IgG Hexamers at the Cell Surface
Abstract
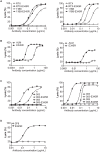
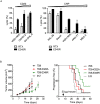
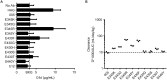
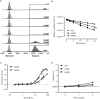
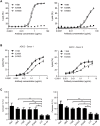
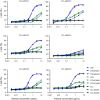
IgG antibodies can organize into ordered hexamers on cell surfaces after binding their antigen. These hexamers bind the first component of complement C1 inducing complement-dependent target cell killing. Here, we translated this natural concept into a novel technology platform (HexaBody technology) for therapeutic antibody potentiation. We identified mutations that enhanced hexamer formation and complement activation by IgG1 antibodies against a range of targets on cells from hematological and solid tumor indications. IgG1 backbones with preferred mutations E345K or E430G conveyed a strong ability to induce conditional complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) of cell lines and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patient tumor cells, while retaining regular pharmacokinetics and biopharmaceutical developability. Both mutations potently enhanced CDC- and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of a type II CD20 antibody that was ineffective in complement activation, while retaining its ability to induce apoptosis. The identified IgG1 Fc backbones provide a novel platform for the generation of therapeutics with enhanced effector functions that only become activated upon binding to target cell-expressed antigen.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: RNdJ, FJB, SV, KS, MV, WH, PJE, SCO, MDvK, JS and PWHIP are Genmab employees and own Genmab warrants and/or stock. RNdJ, FJB, JS and PWHIP are inventors on Genmab patent applications. In this manuscript we described the identification of a new antibody platform for the development of therapeutic antibodies, which we have registered under the trade name “HexaBody.”
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD20 and CD37 antibodies synergize to activate complement by Fc-mediated clustering.Haematologica. 2019 Sep;104(9):1841-1852. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207266. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30792198 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal Antibodies against Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Acquire an Ability To Kill Tumor Cells through Complement Activation by Mutations That Selectively Facilitate the Hexamerization of IgG on Opsonized Cells.J Immunol. 2017 Feb 15;198(4):1585-1594. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601268. Epub 2017 Jan 6. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28062698
-
Antibodies That Efficiently Form Hexamers upon Antigen Binding Can Induce Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity under Complement-Limiting Conditions.J Immunol. 2016 Sep 1;197(5):1762-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600648. Epub 2016 Jul 29. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27474078 Free PMC article.
-
DuoHexaBody-CD37®, a novel biparatopic CD37 antibody with enhanced Fc-mediated hexamerization as a potential therapy for B-cell malignancies.Blood Cancer J. 2020 Apr 28;10(3):30. doi: 10.1038/s41408-020-0292-7. Blood Cancer J. 2020. PMID: 32341336 Free PMC article.
-
New anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of B-cell lymphoid malignancies.BioDrugs. 2011 Feb 1;25(1):13-25. doi: 10.2165/11539590-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2011. PMID: 21090841 Review.
Cited by
-
Complement activation by IgG subclasses is governed by their ability to oligomerize upon antigen binding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 29;121(44):e2406192121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2406192121. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39436656 Free PMC article.
-
An anti-HER2 biparatopic antibody that induces unique HER2 clustering and complement-dependent cytotoxicity.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 13;14(1):1394. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37029-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36914633 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-mediated protection against Ebola virus.Nat Immunol. 2018 Nov;19(11):1169-1178. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0233-9. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30333617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD20 and CD37 antibodies synergize to activate complement by Fc-mediated clustering.Haematologica. 2019 Sep;104(9):1841-1852. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207266. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30792198 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane assembly of aquaporin-4 autoantibodies regulates classical complement activation in neuromyelitis optica.J Clin Invest. 2019 Apr 8;129(5):2000-2013. doi: 10.1172/JCI122942. eCollection 2019 Apr 8. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30958797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melis JP, Strumane K, Ruuls SR, Beurskens FJ, Schuurman J, Parren PW. Complement in therapy and disease: Regulating the complement system with antibody-based therapeutics. Mol Immunol. 2015;67(2 Pt A):117–30. Epub 2015/02/24. 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.01.028 S0161-5890(15)00038-3 [pii]. . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shields RL, Namenuk AK, Hong K, Meng YG, Rae J, Briggs J, et al. High resolution mapping of the binding site on human IgG1 for Fc gamma RI, Fc gamma RII, Fc gamma RIII, and FcRn and design of IgG1 variants with improved binding to the Fc gamma R. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(9):6591–604. Epub 2000/11/30. M009483200 [pii]. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

