Triclosan: A Widespread Environmental Toxicant with Many Biological Effects
- PMID: 26738475
- PMCID: PMC4774862
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010715-103417
Triclosan: A Widespread Environmental Toxicant with Many Biological Effects
Abstract
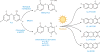
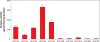
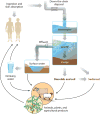
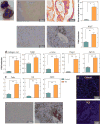
Triclosan (TCS) is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent that has been added to personal care products, including hand soaps and cosmetics, and impregnated in numerous different materials ranging from athletic clothing to food packaging. The constant disposal of TCS into the sewage system is creating a major environmental and public health hazard. Owing to its chemical properties of bioaccumulation and resistance to degradation, TCS is widely detected in various environmental compartments in concentrations ranging from nanograms to micrograms per liter. Epidemiology studies indicate that significant levels of TCS are detected in body fluids in all human age groups. We document here the emerging evidence--from in vitro and in vivo animal studies and environmental toxicology studies--demonstrating that TCS exerts adverse effects on different biological systems through various modes of action. Considering the fact that humans are simultaneously exposed to TCS and many TCS-like chemicals, we speculate that TCS-induced adverse effects may be relevant to human health.
Keywords: antibacterial; antimicrobial resistance; bioaccumulation; environmental hazard; hormone homeostasis; liver pathogenesis; precautionary principle.
Figures
References
-
- Fang JL, Stingley RL, Beland FA, Harrouk W, Lumpkins DL, Howard P. Occurrence, efficacy, metabolism, and toxicity of triclosan. J Environ Sci Health C: Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2010;28:147–71. - PubMed
-
- Rodricks JV, Swenberg JA, Borzelleca JF, Maronpot RR, Shipp AM. Triclosan: a critical review of the experimental data and development of margins of safety for consumer products. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2010;40:422–84. - PubMed
-
- Dann AB, Hontela A. Triclosan: environmental exposure, toxicity and mechanisms of action. J Appl Toxicol. 2011;31:285–311. - PubMed
-
- Wilcox MH, Hall J, Pike H, Templeton PA, Fawley WN, et al. Use of perioperative mupirocin to prevent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) orthopaedic surgical site infections. J Hosp Infect. 2003;54:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Aiello AE, Larson EL, Levy SB. Consumer antibacterial soaps: effective or just risky? Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(Suppl. 2):S137–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

