Doxorubicin nanobubble for combining ultrasonography and targeted chemotherapy of rabbit with VX2 liver tumor
- PMID: 26738862
- PMCID: PMC4990606
- DOI: 10.1007/s13277-015-4525-5
Doxorubicin nanobubble for combining ultrasonography and targeted chemotherapy of rabbit with VX2 liver tumor
Abstract
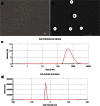
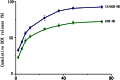
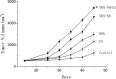
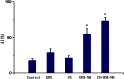
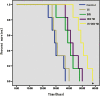
A new class of multifunctional nanobubble using poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) has been developed as ultrasound imaging contrast agents, doxorubicin carriers, and enhancers of ultrasound-mediated drug delivery. The doxorubicin nanobubble (DOX-NB) wrapping carbon tetrafluoride gas was prepared with double emulsion method. We evaluated the enhanced ultrasonic function of the DOX-NB in vivo; its antitumor function was confirmed. The diameter of the prepared bubble was 500 nm, and the potential was -23 mV. The drug loading and encapsulation efficiency of the bubble were 78.6 and 7.4 %, respectively. Therefore, the DOX-NB greatly enhanced ultrasound imaging in vivo. Ultrasound combined with DOX-NB had significant antitumor effect. Compared with other groups, the tumor growth rate and the proliferation index were the lowest while the survival rate and apoptosis index were the highest.
Keywords: Doxorubicin nanobubble (DOX-NB); Treatment; Ultrasound; VX2 liver tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of prostate cancer growth using doxorubicin assisted by ultrasound-targeted nanobubble destruction.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Jul 29;11:3585-96. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S111808. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27536100 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity focused ultrasound mediated localized drug delivery for liver tumors in rabbits.Drug Deliv. 2016 Sep;23(7):2280-2289. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.972528. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 25367869
-
Doxorubicin loaded superparamagnetic PLGA-iron oxide multifunctional microbubbles for dual-mode US/MR imaging and therapy of metastasis in lymph nodes.Biomaterials. 2013 Mar;34(9):2307-17. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23276658
-
Transarterial Infusion of iRGD-Modified ZrO2 Nanoparticles with Lipiodol Improves the Tissue Distribution of Doxorubicin and Its Antitumor Efficacy.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019 Dec;30(12):2026-2035.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2019.04.014. Epub 2019 Oct 4. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31590966
-
Multifunctional nanoparticles for combining ultrasonic tumor imaging and targeted chemotherapy.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007 Jul 18;99(14):1095-106. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djm043. Epub 2007 Jul 10. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007. PMID: 17623798
Cited by
-
A Promising Therapeutic Strategy of Combining Acoustically Stimulated Nanobubbles and Existing Cancer Treatments.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 17;16(18):3181. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183181. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Nanomaterials in Biomedical Imaging and Cancer Therapy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Aug 29;10(9):1700. doi: 10.3390/nano10091700. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sink or float? Characterization of shell-stabilized bulk nanobubbles using a resonant mass measurement technique.Nanoscale. 2019 Jan 17;11(3):851-855. doi: 10.1039/c8nr08763f. Nanoscale. 2019. PMID: 30601524 Free PMC article.
-
Smart stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems in spotlight of COVID-19.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Nov;18(6):100873. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100873. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 38173712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-Responsive Materials for Drug/Gene Delivery.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 31;10:1650. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01650. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32082157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bekeredjian R, Chen S, Frenkel PA, Grayburn PA, Shohet RV. Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction can repeatedly direct highly specific plasmid expression to the heart. Circulation. 2003;108:1022–6. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000084535.35435.AE. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

