Systemic antifungal therapy for proven or suspected invasive candidiasis: the AmarCAND 2 study
- PMID: 26743881
- PMCID: PMC4705061
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-015-0103-7
Systemic antifungal therapy for proven or suspected invasive candidiasis: the AmarCAND 2 study
Abstract
Background: In the context of recent guidelines on invasive candidiasis (IC), how French intensive care units (ICUs) are managing IC?
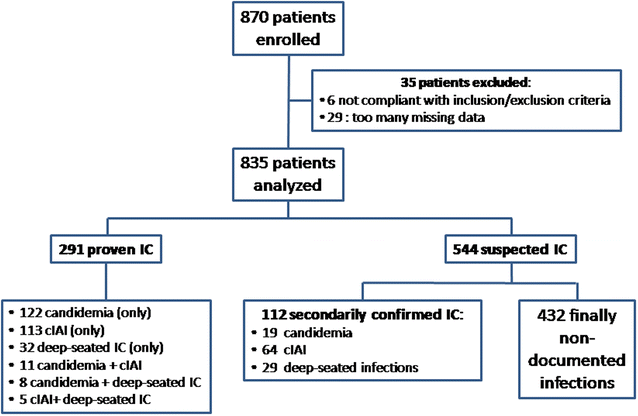
Methods: This is a prospective observational multicenter cohort study. During 1 year (2012-2013), 87 French ICUs enrolled consecutive patients with suspected or proven IC (SIC or PIC) and receiving systemic antifungal therapy (SAT). Data were collected up to 28 days after inclusion.
Results: We studied 835 patients, 291 with PIC and 544 with SIC. At SAT initiation, patients with SIC were significantly more severe (SAPS II 50.1 ± 18.7 vs. 46.2 ± 18.0). Severe sepsis or septic shock prompted to initiate empiric SAT in 70 % of SIC. Within 4 days in median, the initial SAT was modified in 49 % of patients with PIC vs. 33 % patients with SIC. Modifications were most often motivated by mycological results, and de-escalation was the most frequent change. Regarding compliance to IC management guidelines, echinocandin was used for 182 (62.5 %) patients with PIC, and 287 (52.7 %) of those with SIC; central venous catheter was removed in 87 (54.3 %) of patients with candidaemia, and 43 of the remaining patients received echinocandin; and de-escalation was undertaken after 5 days of SAT in 142 patients, after 10 days in 13 patients. As 20.6 % of SIC were secondarily documented, 403/835 (48 %) patients had finally a proven IC. Candida albicans was the main pathogen (65.3 %), then Candida glabrata (15.9 %). The 28-day mortality rates were 40.0 % in candidaemia, 25.4 % in cIAI, and 26.7 % in deep-seated candidiasis. In the overall population of patients with proven IC, four independent prognostic factors were identified: immunosuppression (Odds Ratio (OR) = 1.977: 1.03-3.794 95 % confidence interval (CI), p = 0.04), age (OR = 1.035; 1.017-1.053 95 % CI; p < 0.001), SAPS >46 on ICU admission (OR = 2.894; 1.81-4.626 95 % CI; p < 0.001), and surgery just before or during ICU stay (OR = 0.473; 0.29-0.77 95 % CI; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: When SAT is initiated in French ICUs, the IC is ultimately proven for 48 % of patients. Empiric SAT is initiated in severely ill ICU patients. The initial SAT is often adapted, with de-escalation to fluconazole when possible. Mortality rate remains high.
Keywords: Candida; Candidaemia; Candidiasis; Cohort study; Critically ill; Intensive care.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials