Mitochondria in Kidney Injury: When the Power Plant Fails
- PMID: 26744487
- PMCID: PMC4926990
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015111277
Mitochondria in Kidney Injury: When the Power Plant Fails
Keywords: acute renal failure; ischemia-reperfusion; mitochondria; nephrotoxicity.
Figures
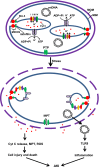
Comment on
-
Role of Mitochondrial DNA in Septic AKI via Toll-Like Receptor 9.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jul;27(7):2009-20. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015040376. Epub 2015 Nov 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26574043 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochonic Acid 5 Binds Mitochondria and Ameliorates Renal Tubular and Cardiac Myocyte Damage.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jul;27(7):1925-32. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015060623. Epub 2015 Nov 25. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26609120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suzuki T, Yamaguchi H, Kikusato M, Hashizume O, Nagatoishi S, Matsuo A, Sato T, Kudo T, Matsuhashi T, Murayama K, Ohba Y, Watanabe S, Kanno SI, Minaki D, Saigusa D, Shinbo H, Mori N, Yuri A, Yokoro M, Mishima E, Shima H, Akiyama Y, Takeuchi Y, Kikuchi K, Toyohara T, Suzuki C, Ichimura T, Anzai JI, Kohzuki M, Mano N, Kure S, Yanagisawa T, Tomioka Y, Tohyomizu M, Tsumoto K, Nakada K, Bonventre JV, Ito S, Osaka H, Hayashi KI, Abe T: Mitochonic Acid 5 Binds Mitochondria and Ameliorates Renal Tubular and Cardiac Myocyte Damage. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:1925–1932, 2016 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Che R, Yuan Y, Huang S, Zhang A: Mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathophysiology of renal diseases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 306: F367–F378, 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

